Respiration in Plants - Plants, like all living organisms, require energy to function and grow. This energy fuels vital processes like nutrient uptake, growth, and defense against environmental threats. But unlike animals who rely solely on consuming external food sources, plants have a unique ability to manufacture their own food through photosynthesis. However, photosynthesis isn't the whole story. Plants also undergo a fundamental process called respiration to tap into the energy they've created.
What is Respiration in Plants?
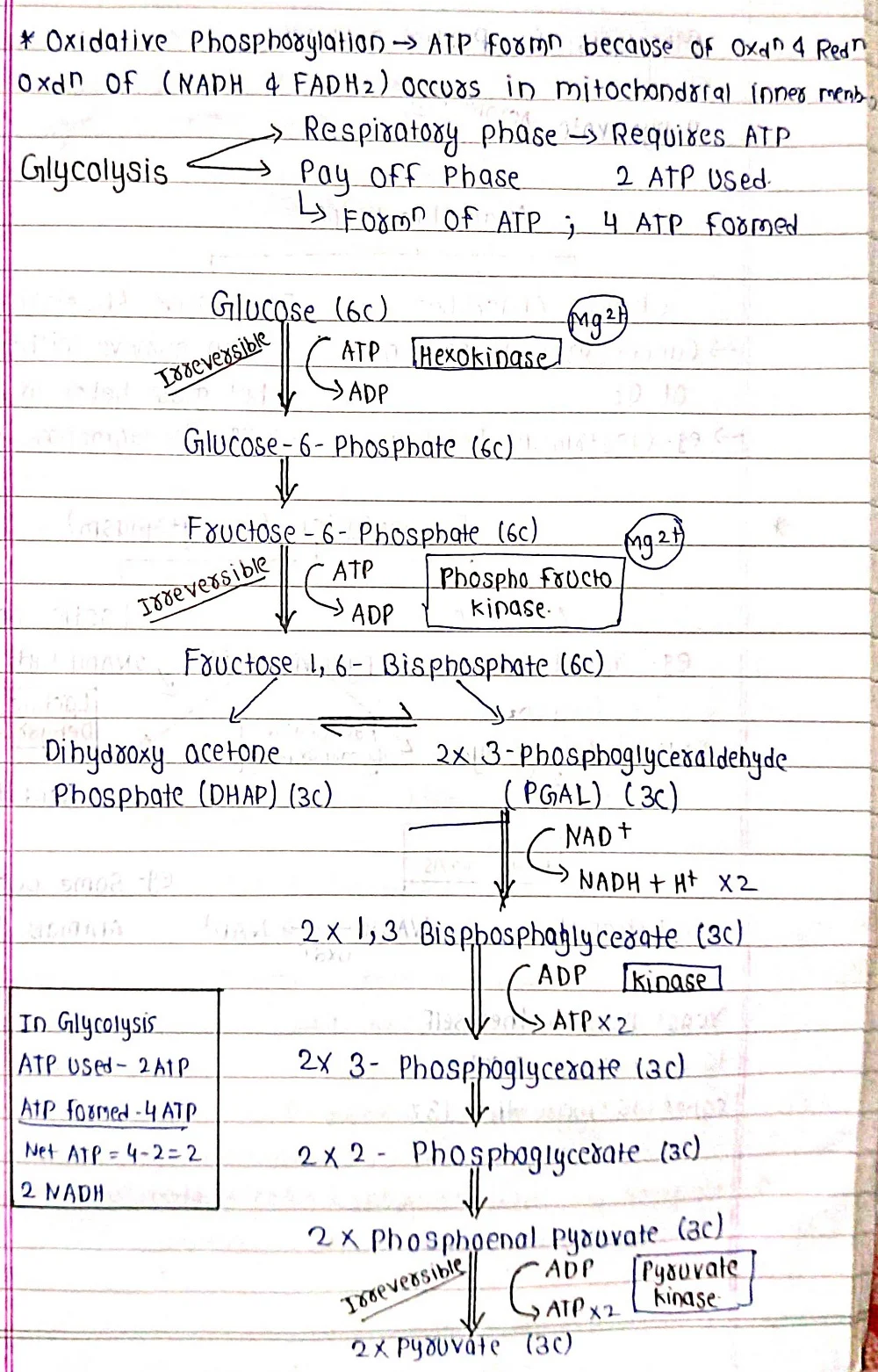
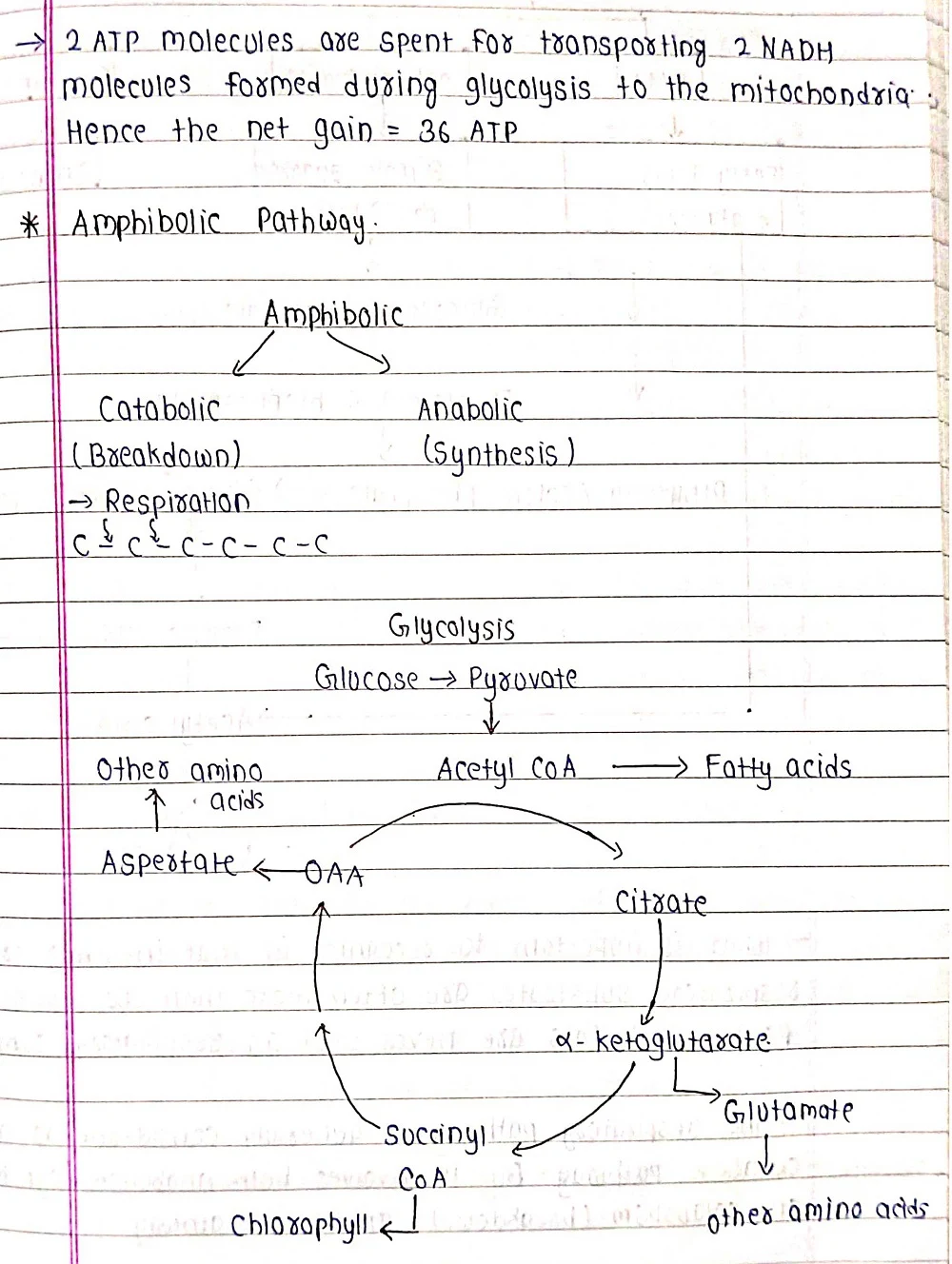
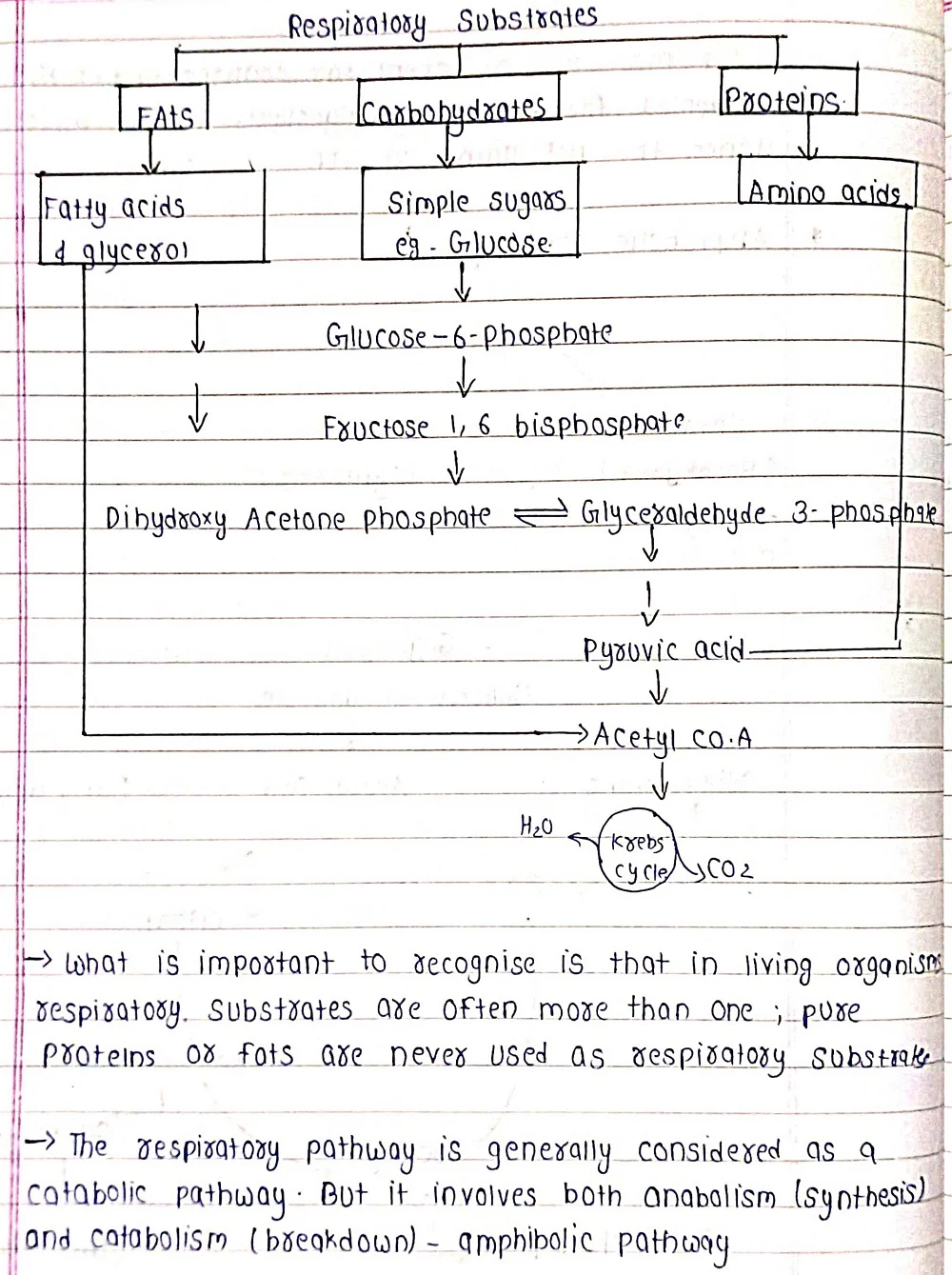
Respiration is a cellular process that breaks down organic molecules, like glucose (produced during photosynthesis), in the presence of oxygen to release energy. This energy is then captured in a usable form, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which powers various cellular activities. In simpler terms, respiration is like cellular "breathing" – it takes in oxygen and releases carbon dioxide, similar to animals, but with the crucial difference that plants use the energy for their own internally produced food source.
Types of Respiration in Plants
There are two main types of respiration that occur in plants:
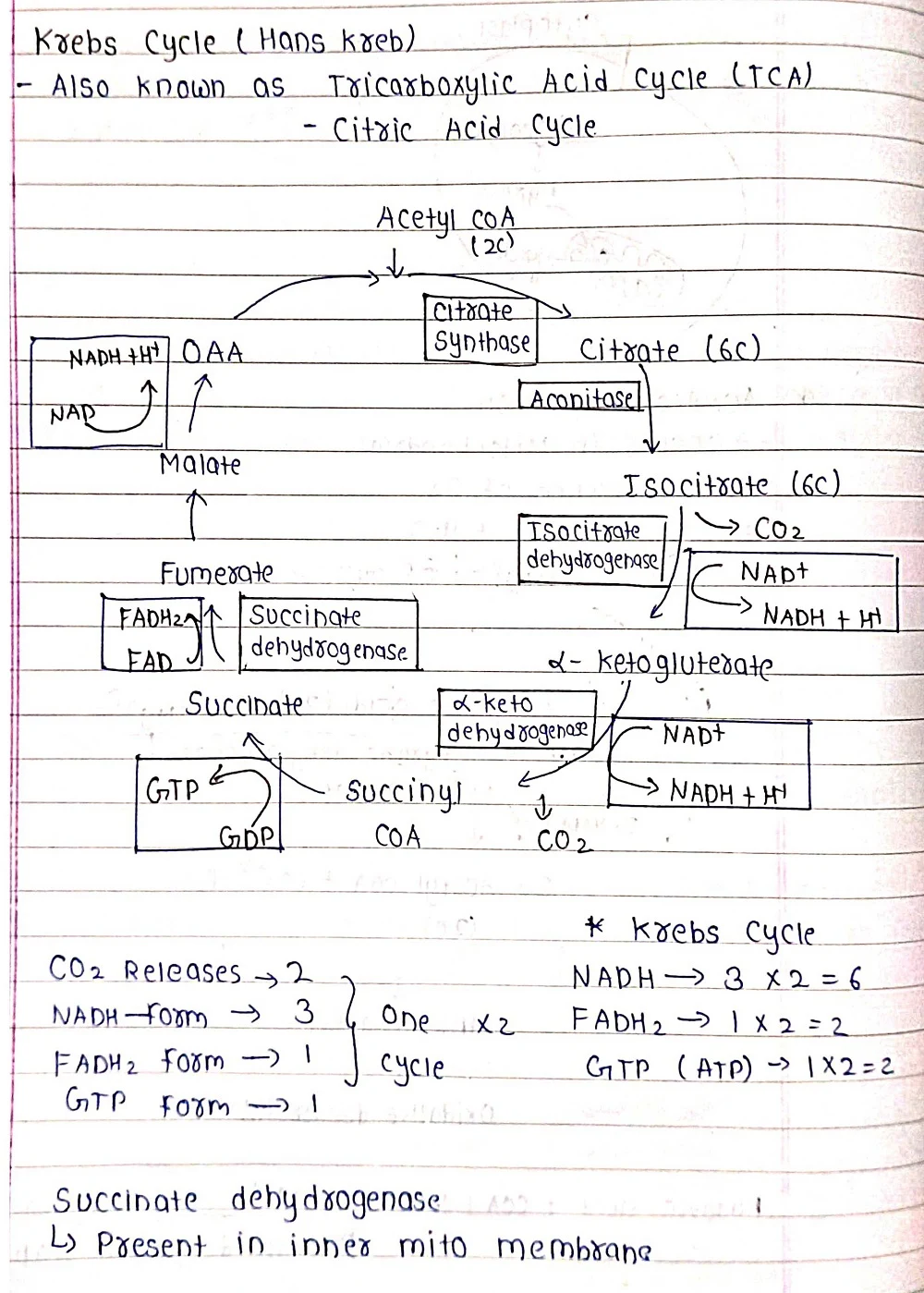
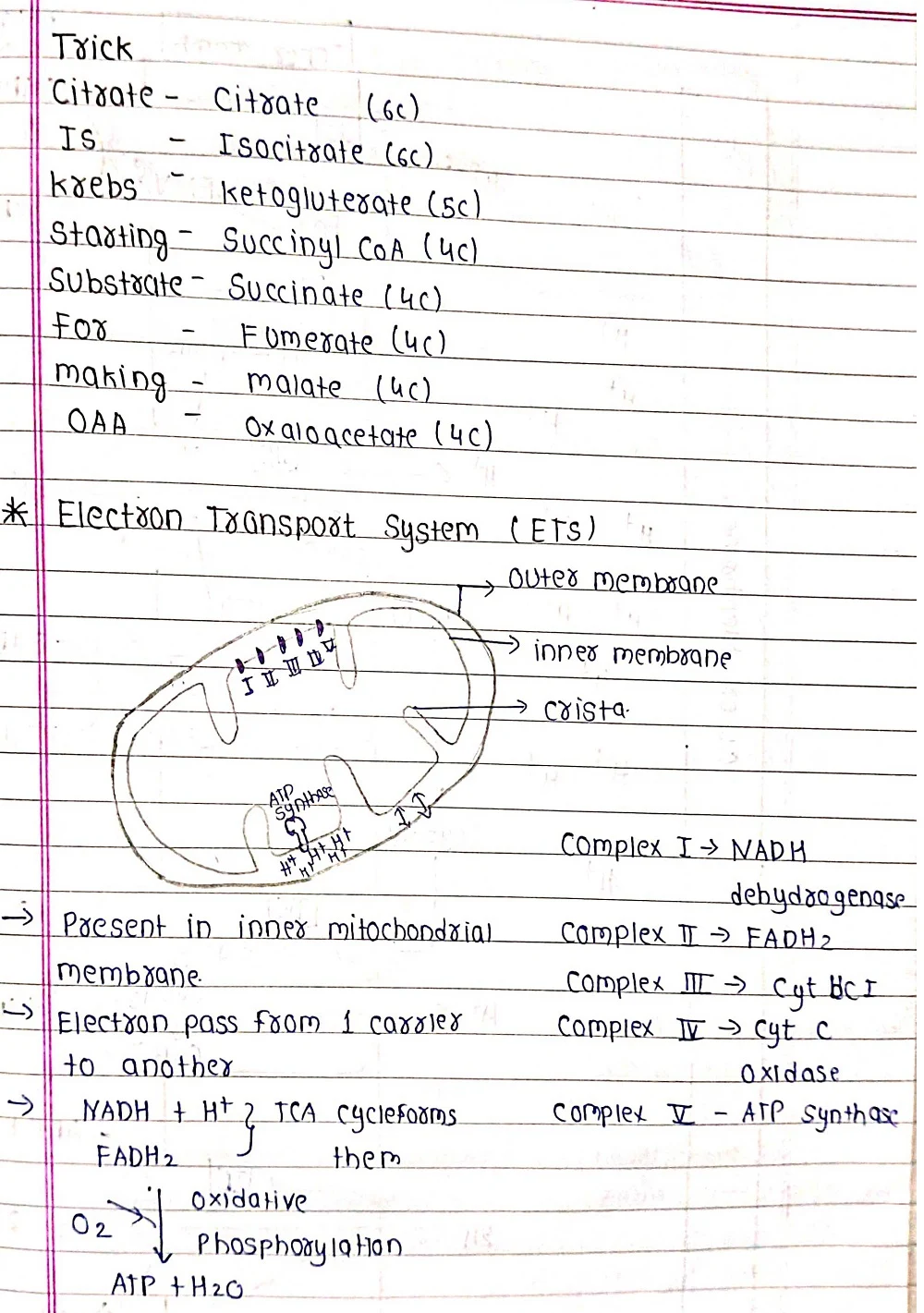
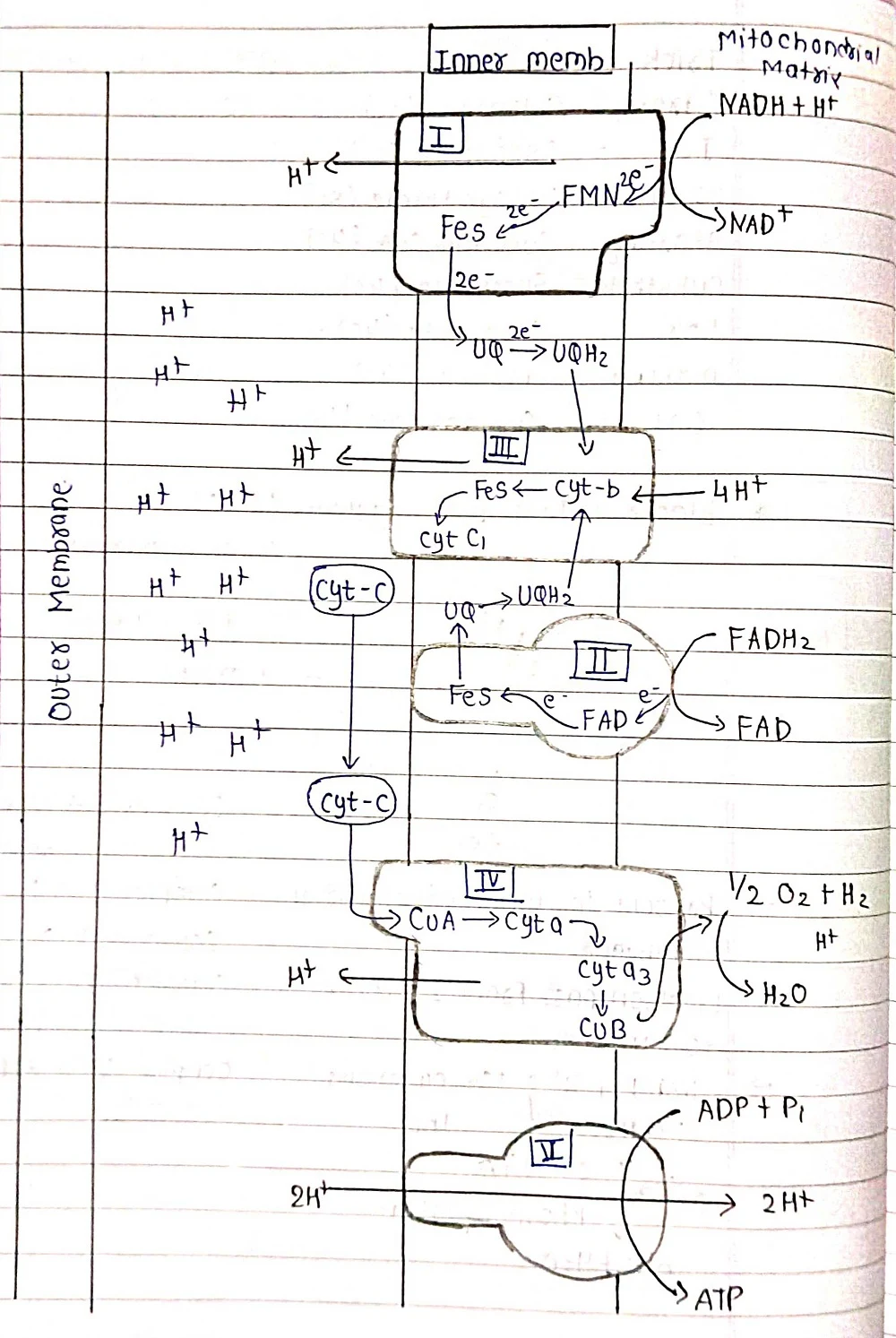
⦿Aerobic Respiration: This is the primary mode of respiration and requires oxygen. It occurs in the mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell, and follows a well-defined pathway involving multiple steps to break down glucose and generate ATP.
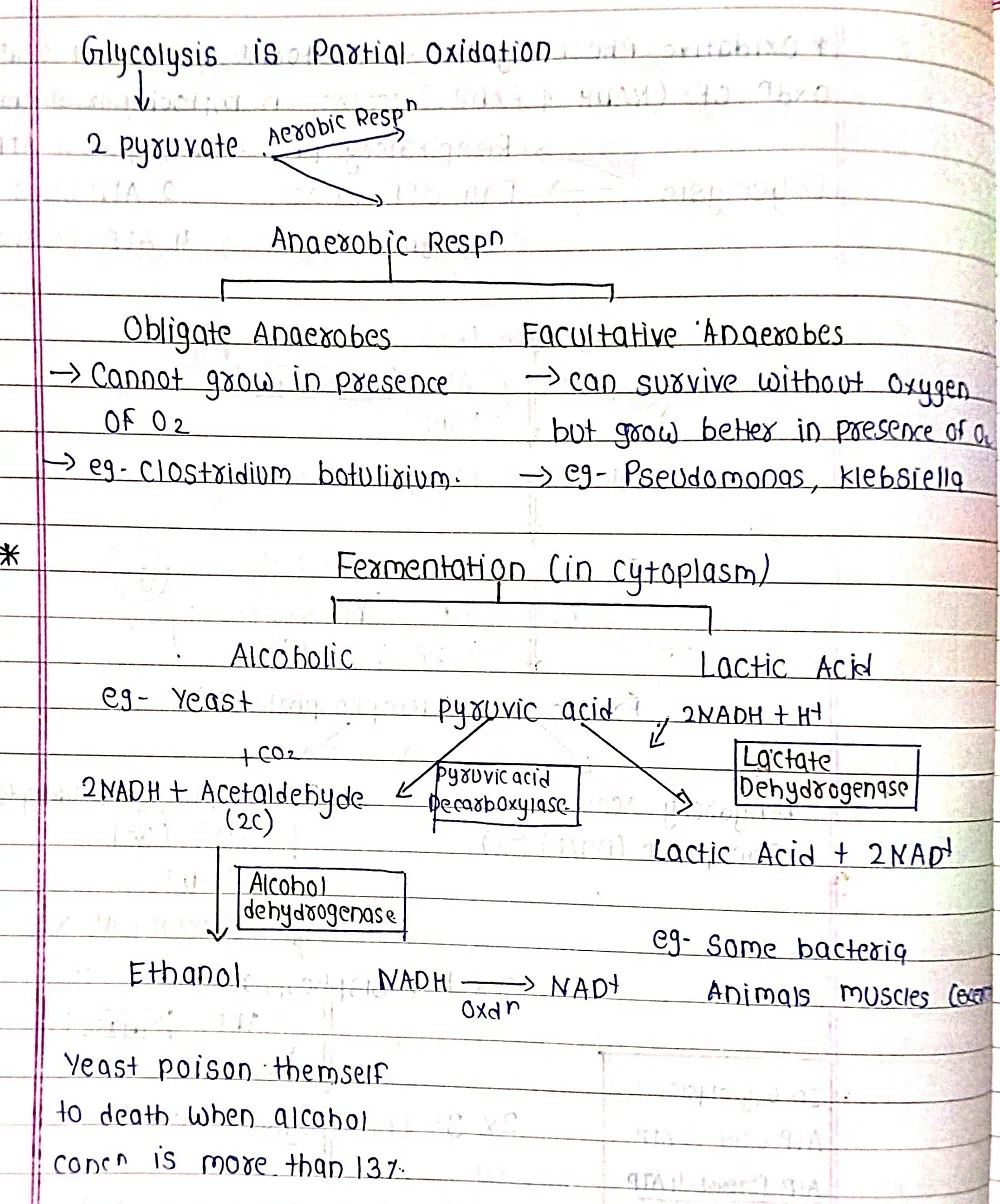
⦿Anaerobic Respiration: This is a secondary process that occurs in the absence of oxygen, often in plant roots submerged in waterlogged soil. It's less efficient than aerobic respiration and produces less ATP. During anaerobic respiration, glucose is fermented into products like ethanol or lactic acid.
Examples of Respiration in Plants
Respiration is essential for all plant functions. Here are some specific examples:
⦿Seed Germination: Seeds require a burst of energy to break out of their dormancy and germinate. Respiration provides the ATP needed for this process.
⦿Growth and Development: The energy derived from respiration fuels the growth of roots, stems, and leaves.
⦿Nutrient Uptake: Plants use energy from respiration to actively transport nutrients from the soil into their roots.
⦿Maintaining Cellular Functions: All cellular activities, including protein synthesis and waste removal, require energy from respiration.
Applications of Understanding Plant Respiration
Understanding plant respiration has several crucial applications in agriculture and horticulture:
⦿Optimizing Crop Growth: By understanding the factors affecting plant respiration rates, such as temperature and oxygen availability, growers can create ideal conditions for maximum crop yield.
⦿Improving Storage Practices: Understanding how respiration affects the spoilage of fruits and vegetables helps develop better storage methods to extend their shelf life.
⦿Engineering Stress-Tolerant Plants: Research on the role of respiration in response to environmental stress can lead to the development of crops that are more resistant to drought, flooding, or other challenges.
In conclusion, respiration is a fundamental process in plants that works hand-in-hand with photosynthesis to sustain life. By delving deeper into the intricacies of plant respiration, we can not only unlock a greater understanding of plant biology but also find ways to improve agricultural practices and ensure a more sustainable food system.
FAQ about Respiration in Plants
1. Do plants breathe like animals?
Plants and animals both take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide. However, plants use the oxygen to break down food they produce themselves (glucose from photosynthesis) for energy, while animals take in oxygen to break down external food sources.
2. Where does respiration occur in plants?
Respiration primarily occurs in the mitochondria of plant cells, similar to animal cells.
3. Is photosynthesis the opposite of respiration?
In a way, yes. Photosynthesis uses sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create glucose and releases oxygen. Respiration breaks down glucose and oxygen to release energy and carbon dioxide.
4. Can plants survive without respiration?
No. Although photosynthesis provides the initial food source (glucose), respiration is essential for converting that food into usable energy for all cellular functions. Without respiration, plants wouldn't have the energy to grow, develop, or even stay alive.
5. What factors affect the rate of respiration in plants?
Several factors influence respiration rates, including temperature (increases with higher temperatures), oxygen availability (lower oxygen levels lead to slower rates), and plant age (younger tissues typically respire faster).