The p-block elements are a fascinating group occupying the rightmost side of the periodic table (groups 13-18). They hold immense significance in various fields, from forming the building blocks of life to powering our technological advancements. Here's a quick overview to get you started:
P-Block Elements: An Overview
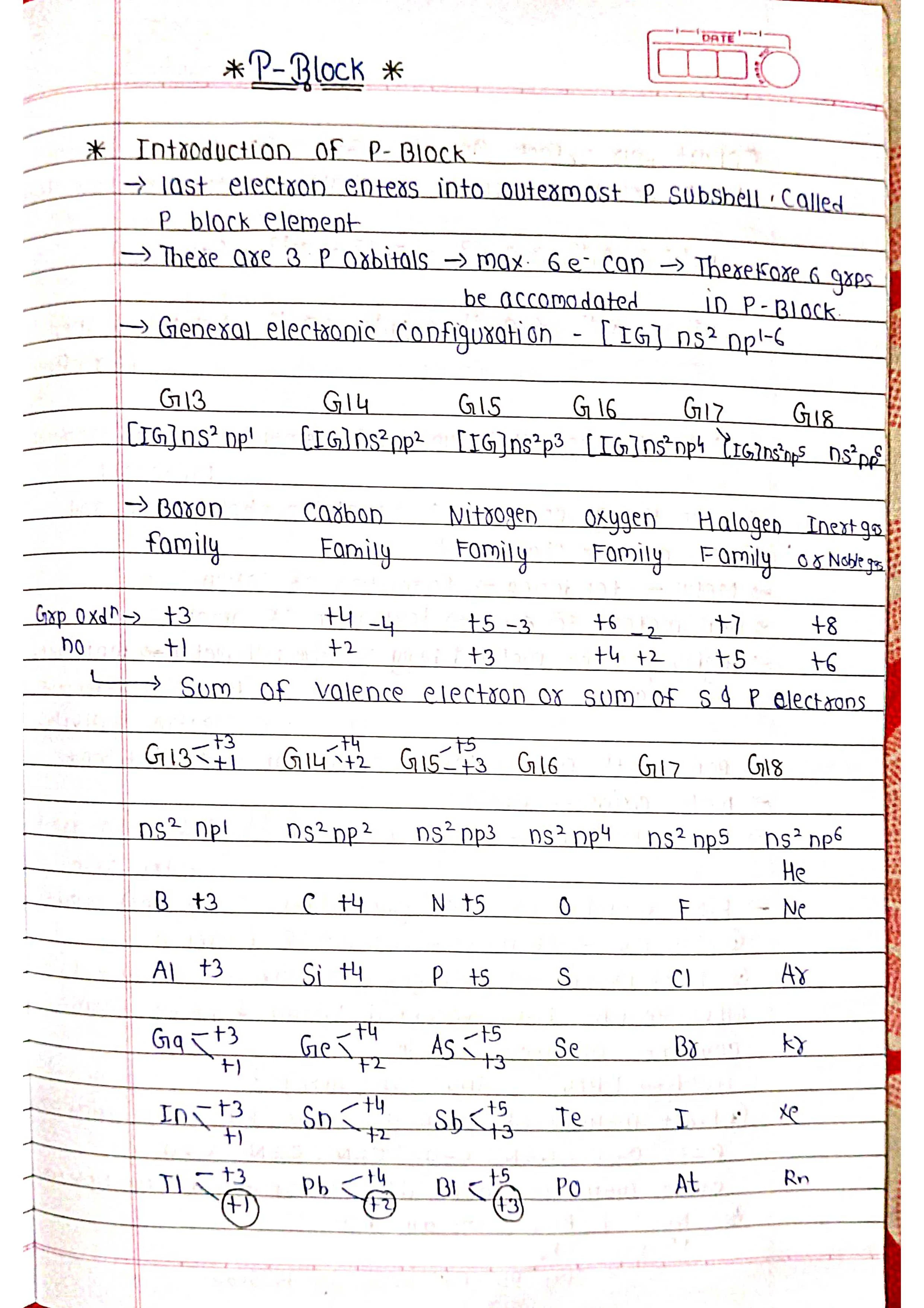
➭ Definition: P-block elements are those in the periodic table where the last electron enters the outermost p-subshell. They occupy groups 13 to 18 (excluding He in group 18).
➭ Location: Refer to the periodic table to visualize their positions.
➭ Classification: They encompass metals, non-metals, and metalloids, exhibiting diverse properties.
Key Characteristics of P-Block Elements
➭ Electron Configuration: Their outermost electronic configuration ends in ns2np<sup>x</sup>, where n is the principal quantum number and x varies from 1 to 6 depending on the group.
➭ Oxidation States: They exhibit a wide range of oxidation states, from -3 to +7, due to the varying number of valence electrons in their p-orbitals.
➭ Allotropy: Many p-block elements exhibit allotropy, meaning they can exist in different physical forms with different properties (e.g., carbon as graphite and diamond).
➭ Trends: Moving down a group:
- Metallic character increases.
- Ionization energy decreases.
- Electronegativity decreases.
- Atomic radius increases.
- Melting and boiling points generally increase.
Important P-Block Families
➭ Group 13 (Boron Family): B, Al, Ga, In, Tl
➡️ Properties: Shiny, ductile, malleable.
➡️ Uses: Boron (semiconductors), aluminum (alloys), gallium (thermometers), indium (display screens), thallium (pesticides).
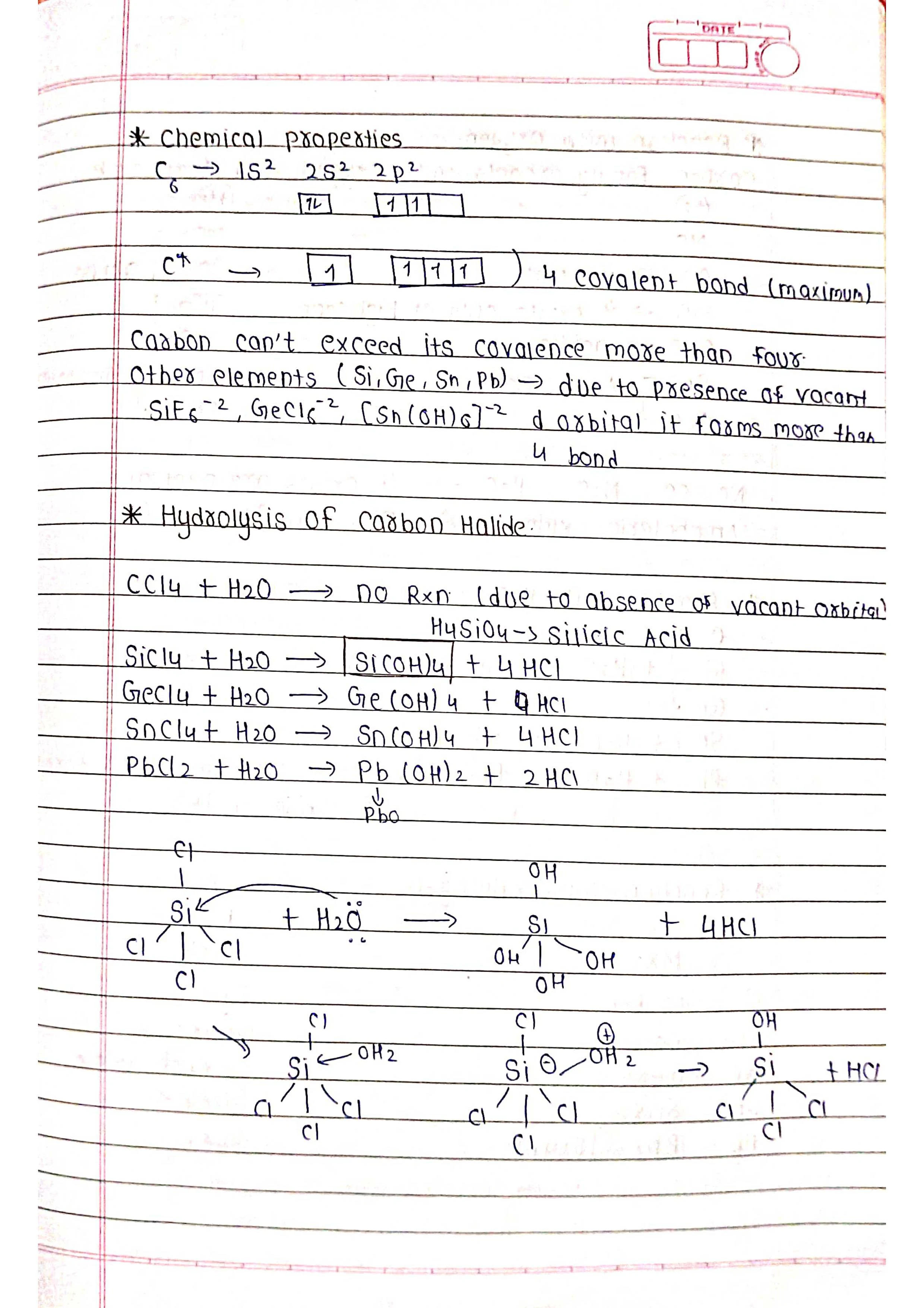
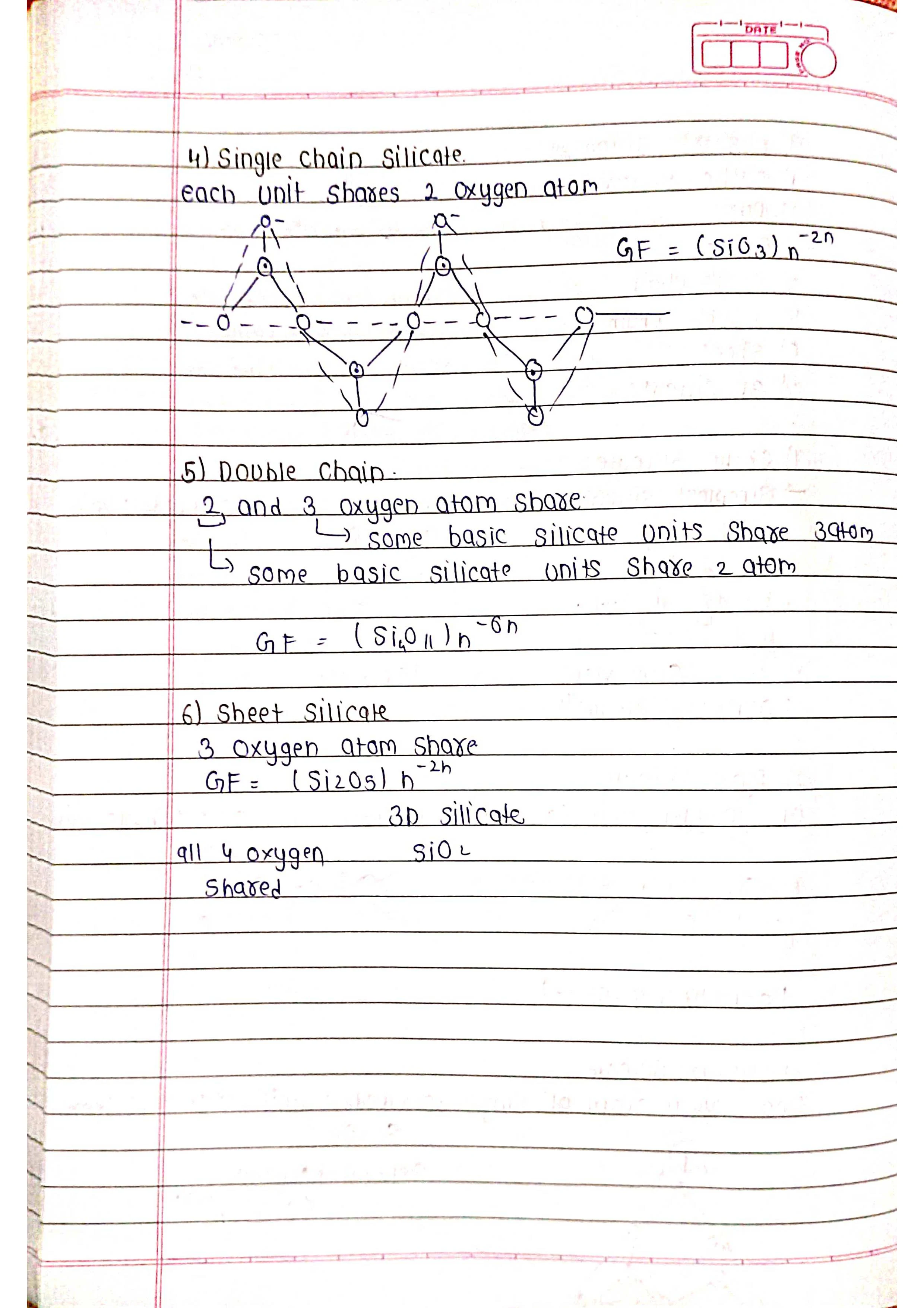
➭ Group 14 (Carbon Family): C, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb
➡️ Properties: Varied (non-metals, metalloids, metals).
➡️ Uses: Carbon (diamond, graphite, coal), silicon (semiconductors), germanium (transistors), tin (soldering), lead (batteries).
➭ Group 15 (Nitrogen Family): N, P, As, Sb, Bi
➡️ Properties: Varied (non-metals, metalloids, metals).
➡️ Uses: Nitrogen (air, fertilizers), phosphorus (bones, DNA), arsenic (pesticides), antimony (alloys), bismuth (pharmaceuticals).
➭ Group 16 (Oxygen Family): O, S, Se, Te, Po
➡️ Properties: Non-metals or metalloids.
➡️ Uses: Oxygen (air, respiration), sulfur (sulfuric acid), selenium (photovoltaic cells), tellurium (alloys), polonium (radioactive).
➭ Group 17 (Halogens): F, Cl, Br, I, At
➡️ Properties: Highly reactive non-metals.
➡️ Uses: Fluorine (toothpaste), chlorine (disinfectant), bromine (fire retardants), iodine (antiseptic), astatine (radioactive).
➭ Group 18 (Noble Gases): He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
➡️ Properties: Inert gases with stable electron configurations.
➡️ Uses: Helium (balloons), neon (signs), argon (incandescent bulbs), krypton (lasers), xenon (anesthetics), radon (radioactive).
Chemistry Short Notes 📚⌛
1. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Short Notes 📚
2. Atomic Structure — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
3. Periodic table — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
4. Chemical Bonding — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
5. States of matter — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
6. Thermodynamics — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
7. Chemical Equilibrium — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
8. Ionic Equilibrium — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
9. Redox Reaction — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
10. Hydrogen — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
11. S-Block Elements - Chemistry Short Notes 📚


![P-Block Elements 1 - Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF]📚 P-Block Elements 1 - Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF]📚](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjkp2mr0ETjCQ7f4a-H35Aj4t8mAeNVQuAngpqeRlZovnJu64jK_xBGzuUgWLyxpeWekxC8kPbl5M-086VJcjAtm_axHHpbx17UiYIloFYTBQO47UHaBmFeKARY3vjcS0vy71NrFYJAK_Urbb2qwvdZlDgveObrme9bmSUPmT8vuBsPUBPhf54ey8jU314/s16000-rw/P-Block%20Elements%201%20-%20Chemistry%20Short%20Handwritten%20Notes%20%5BPDF%5D%F0%9F%93%9A.jpeg)