IUPAC nomenclature, developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, is a systematic method for naming chemical compounds. It ensures clarity and consistency in communication across different languages and disciplines. Here's a quick overview:
IUPAC Nomenclature - Key Principles
Unique and unambiguous: Each name corresponds to a single structure, and vice versa.
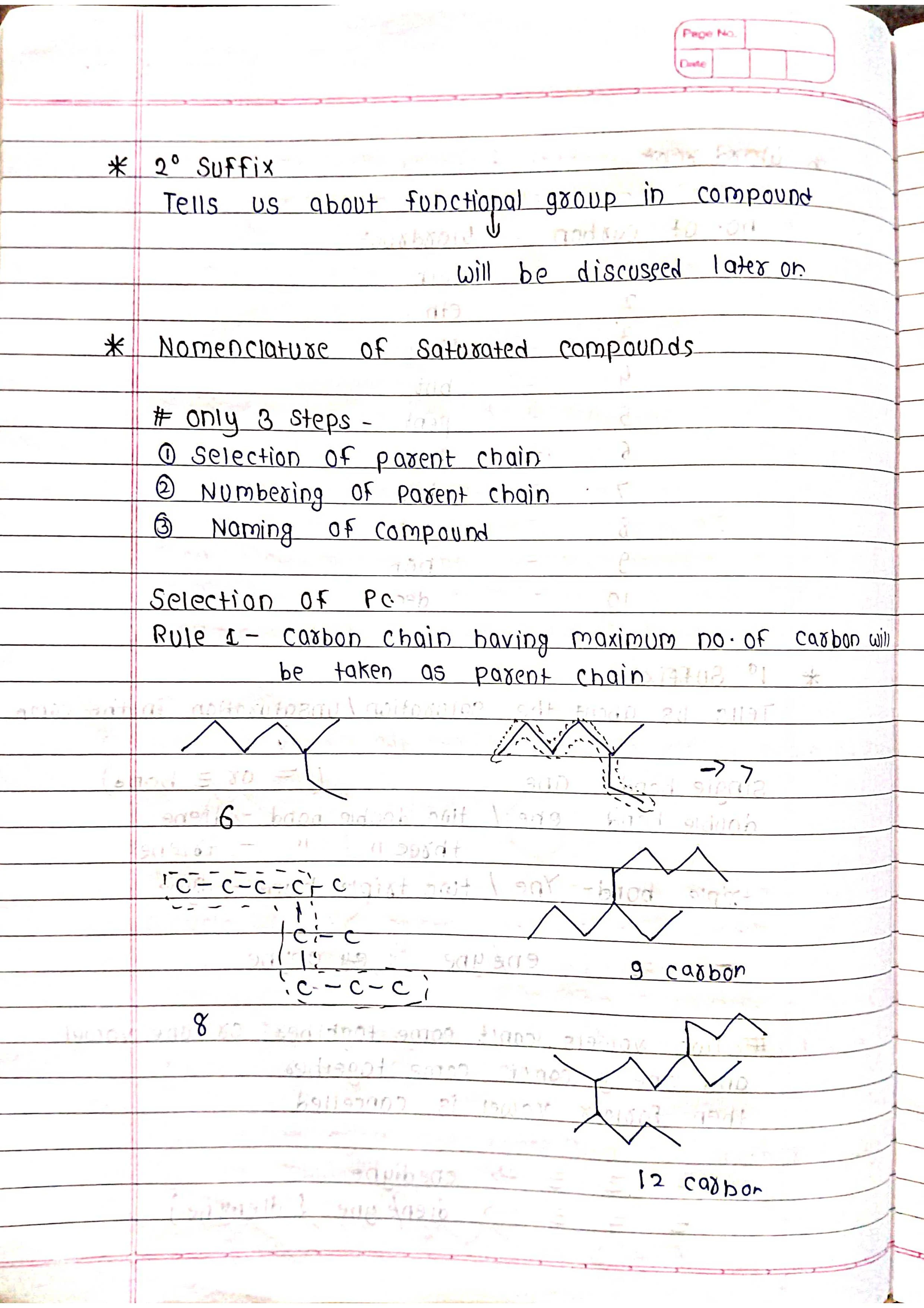
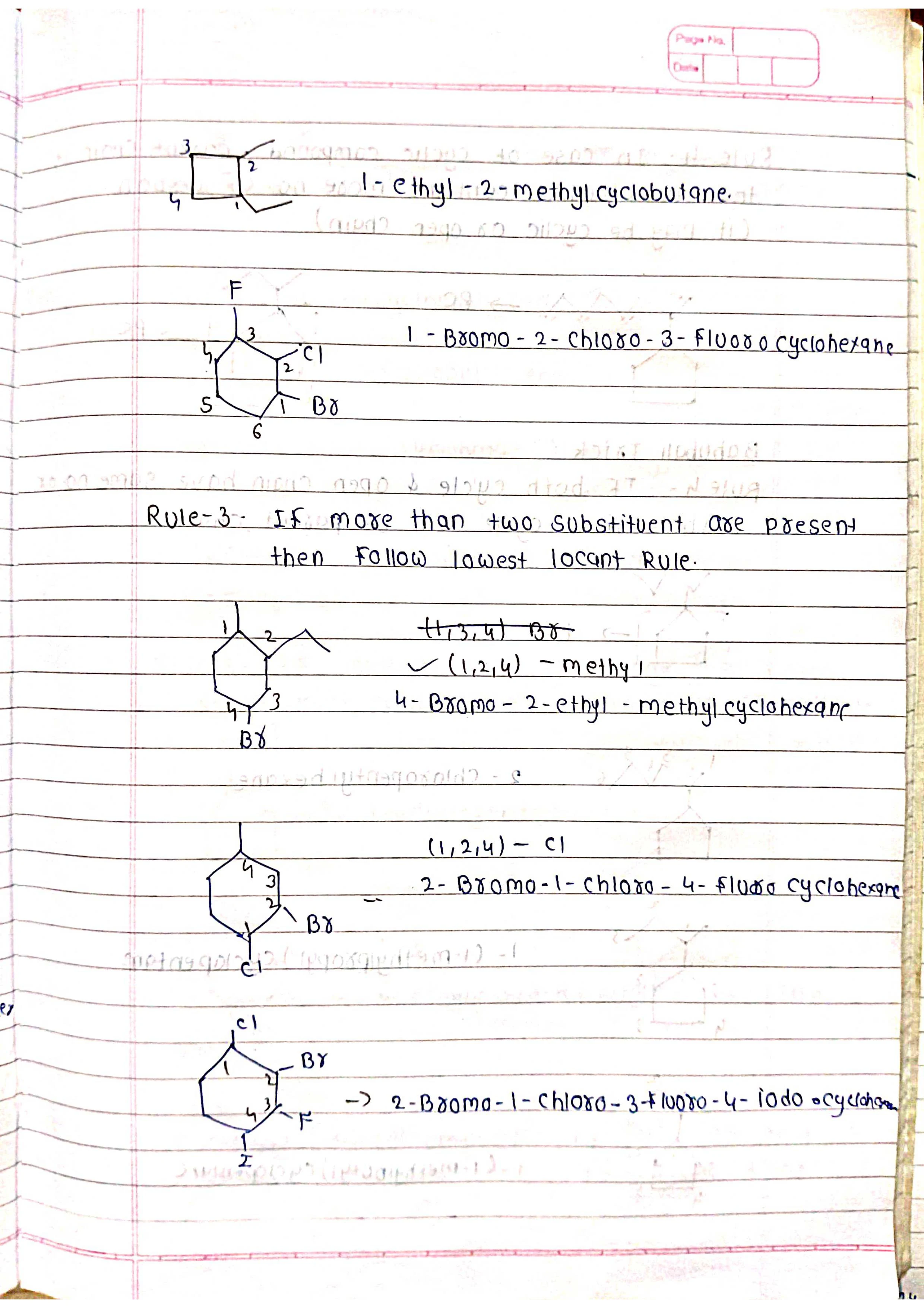
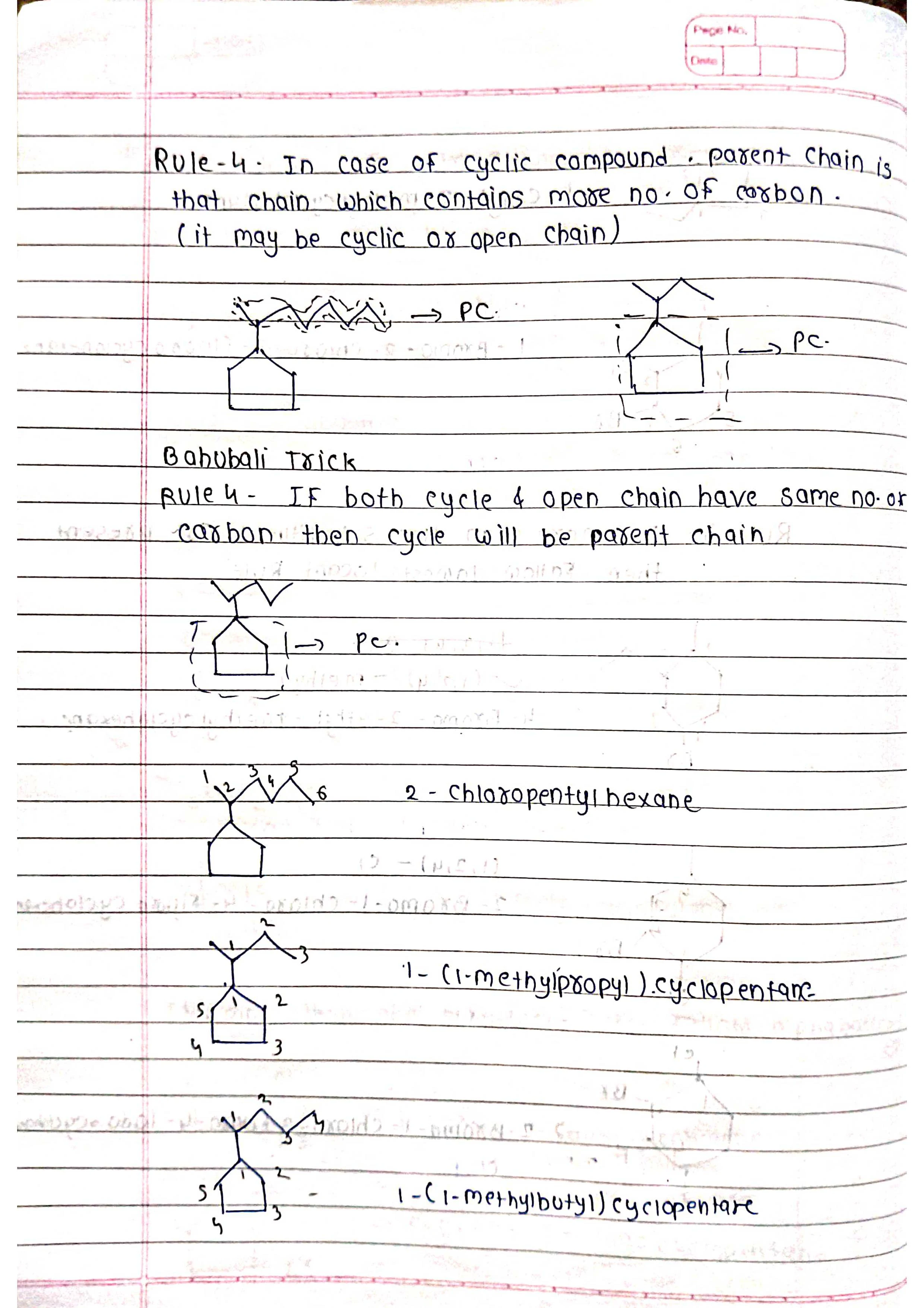
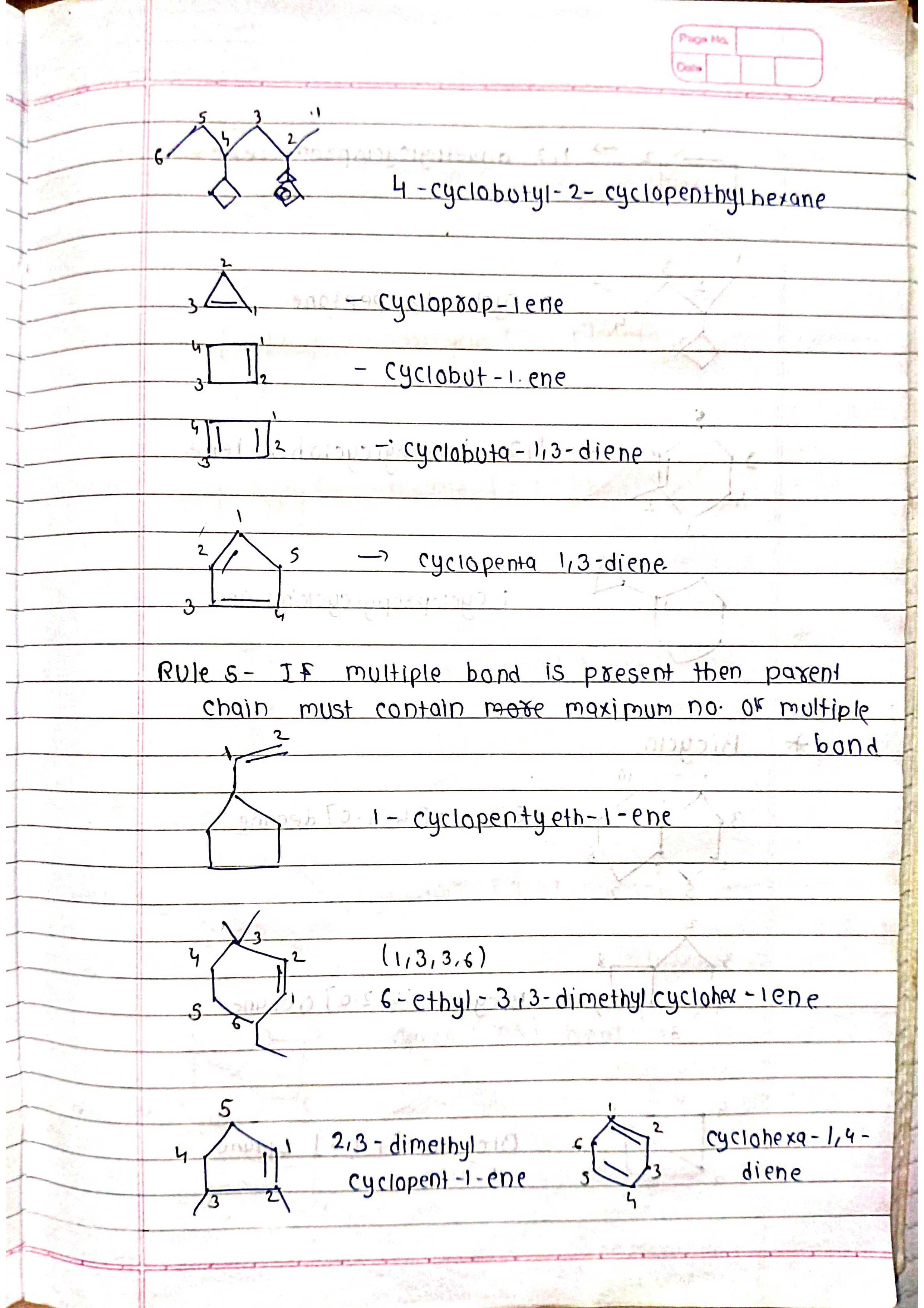
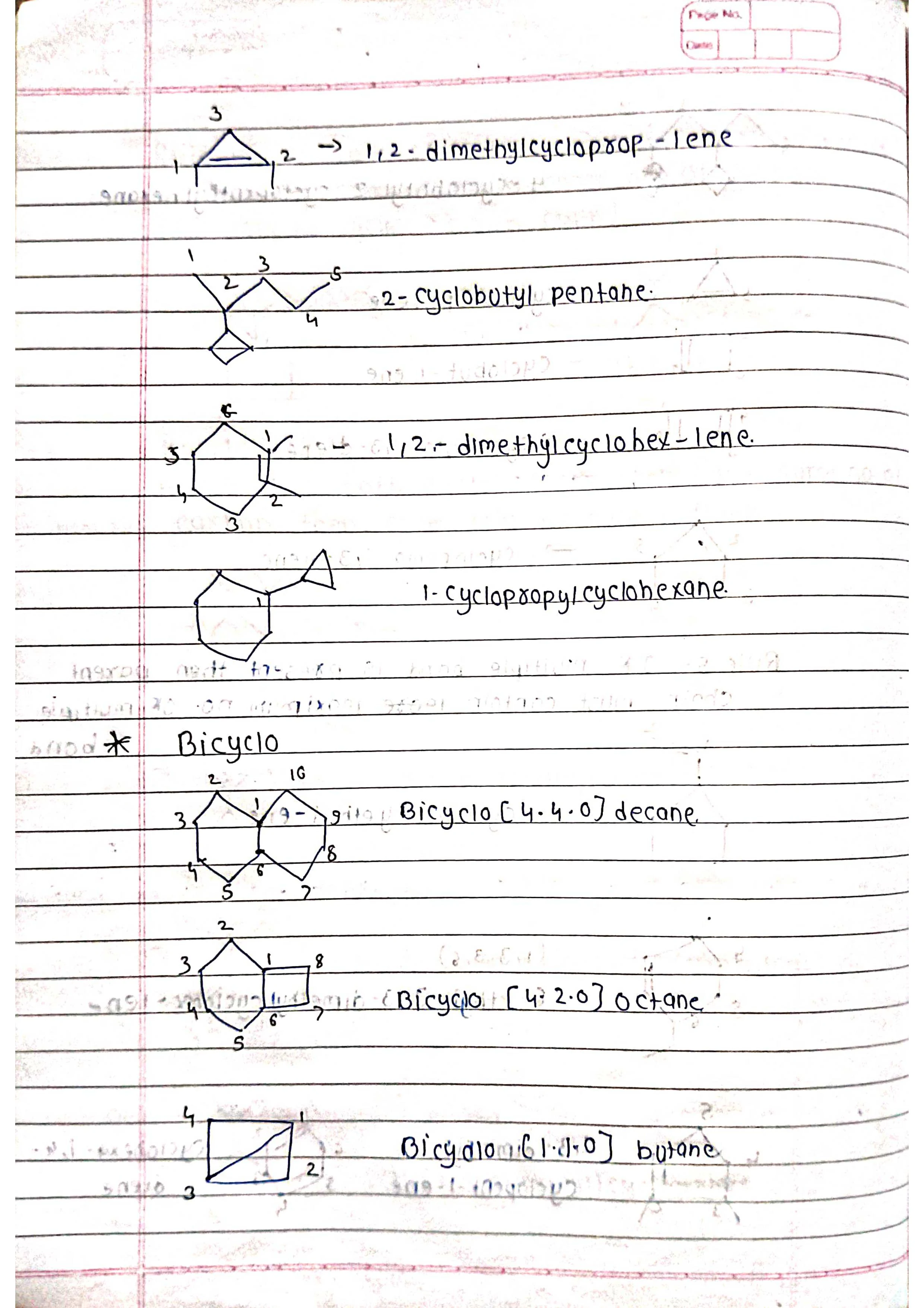
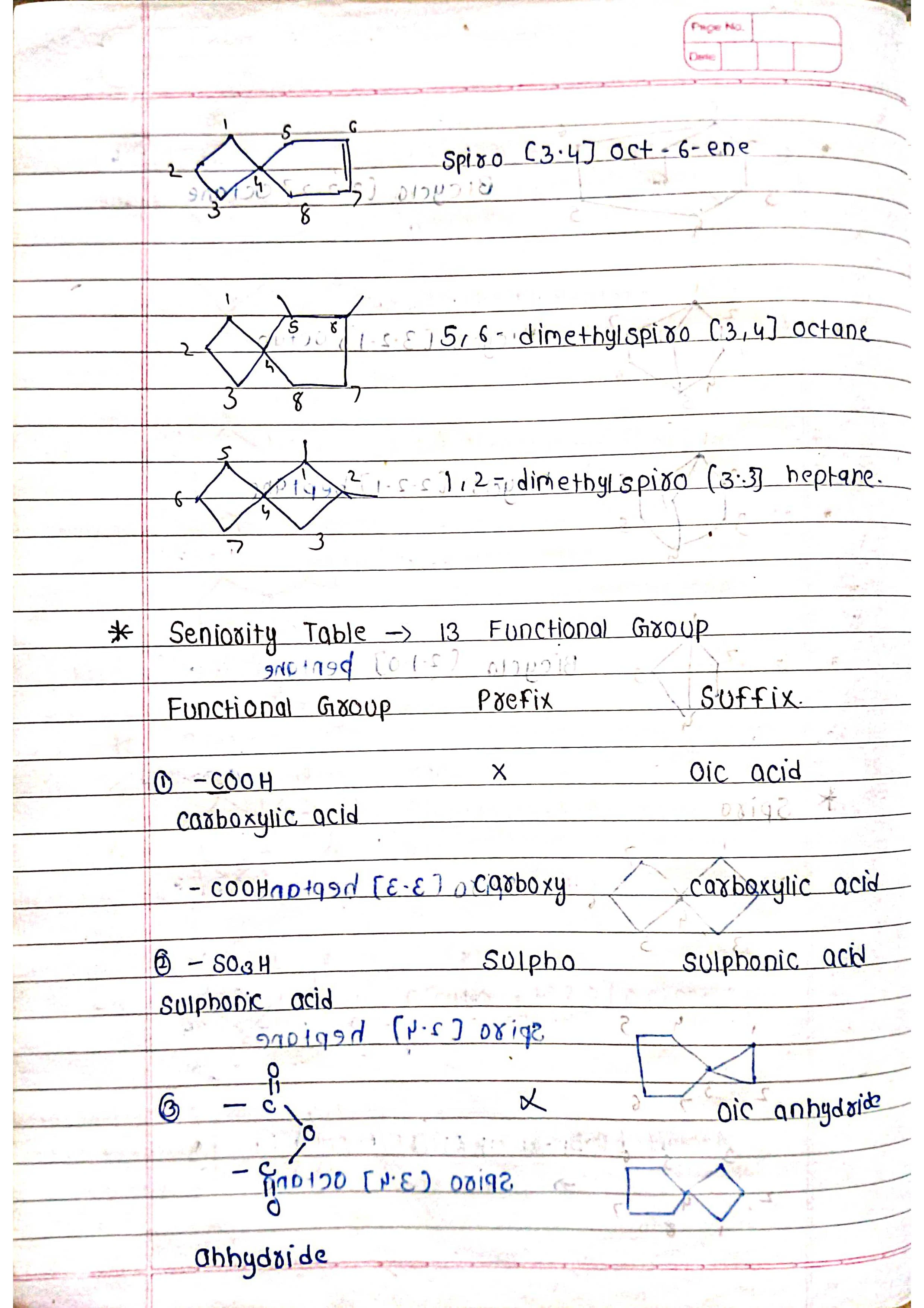
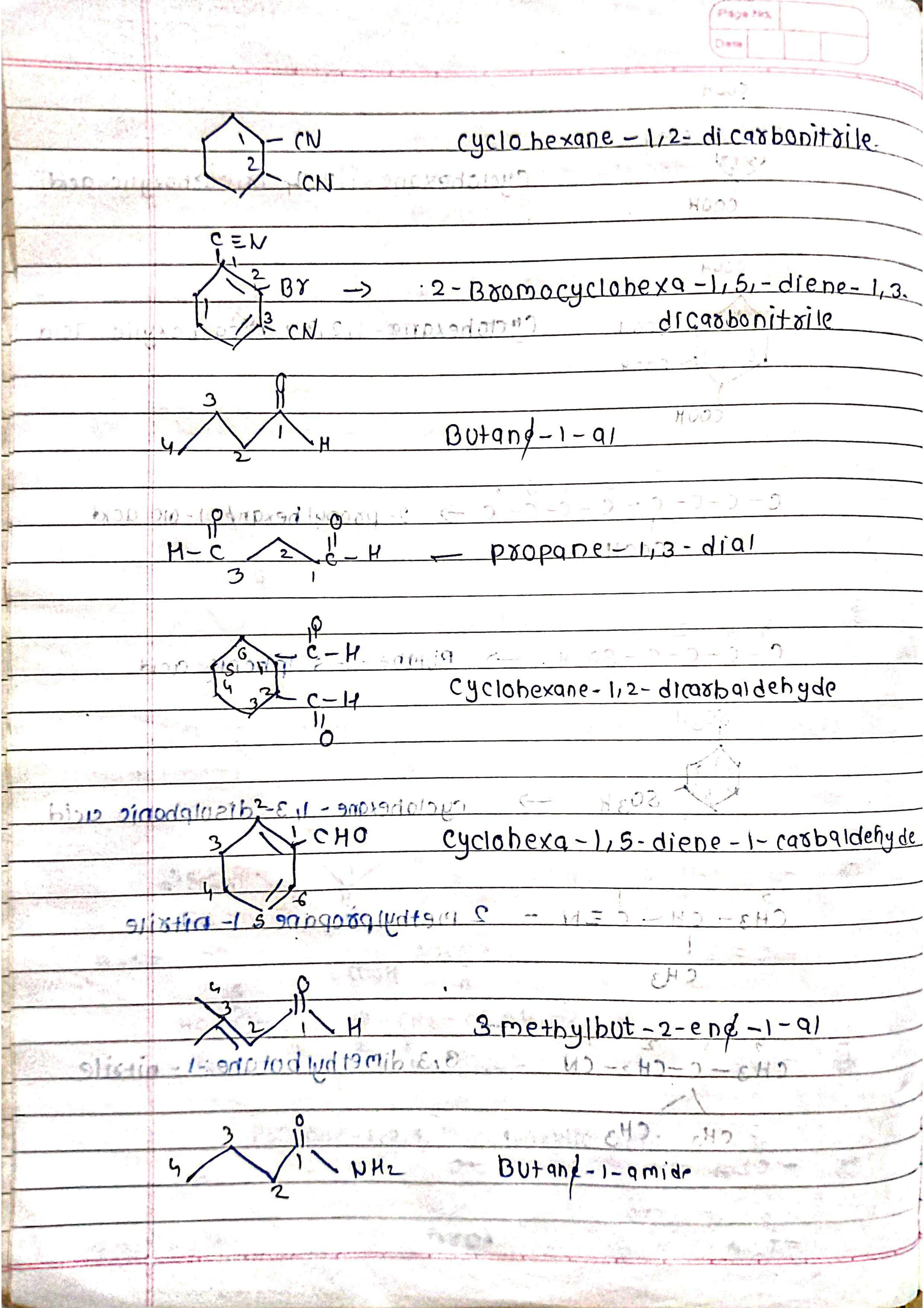
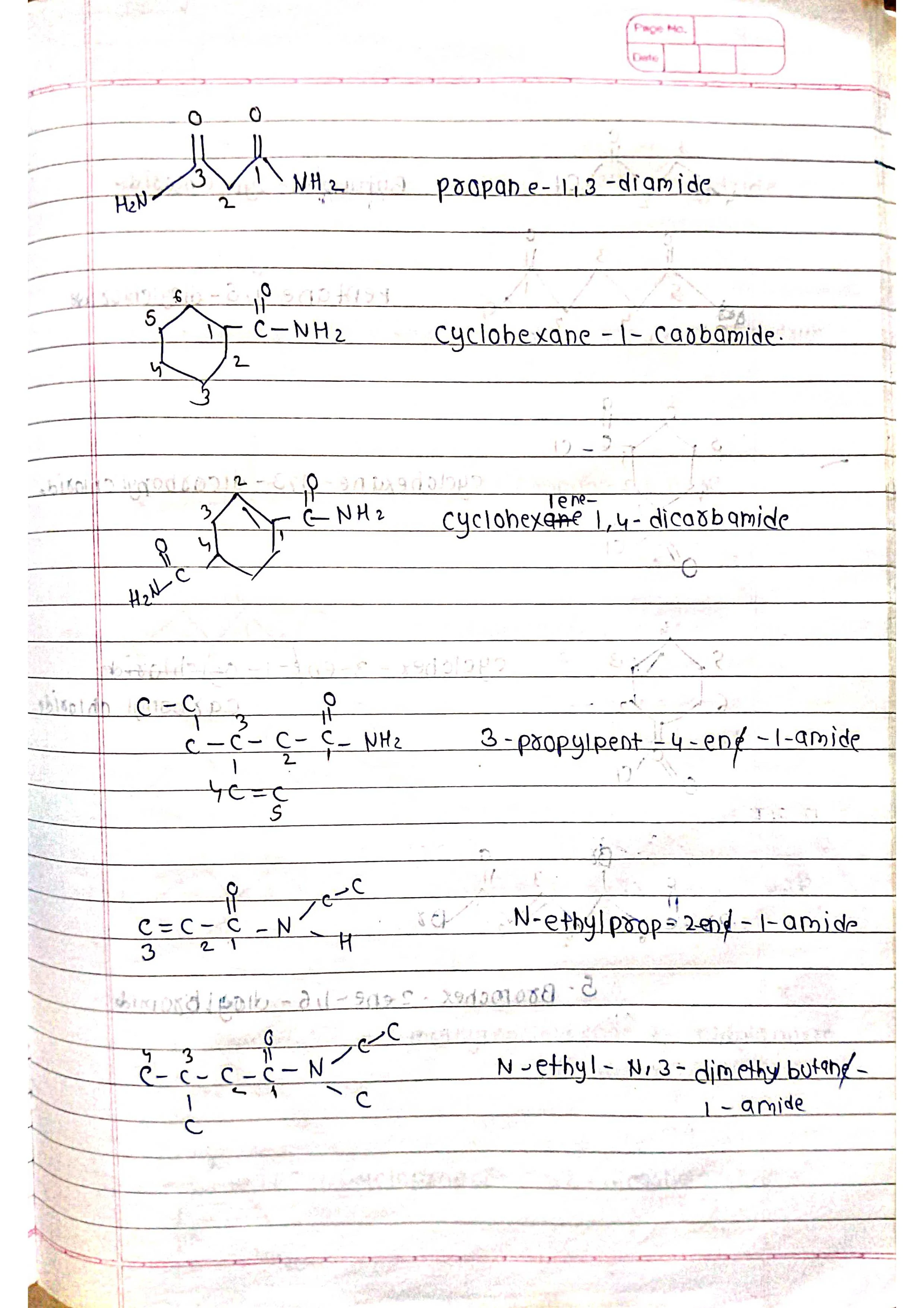
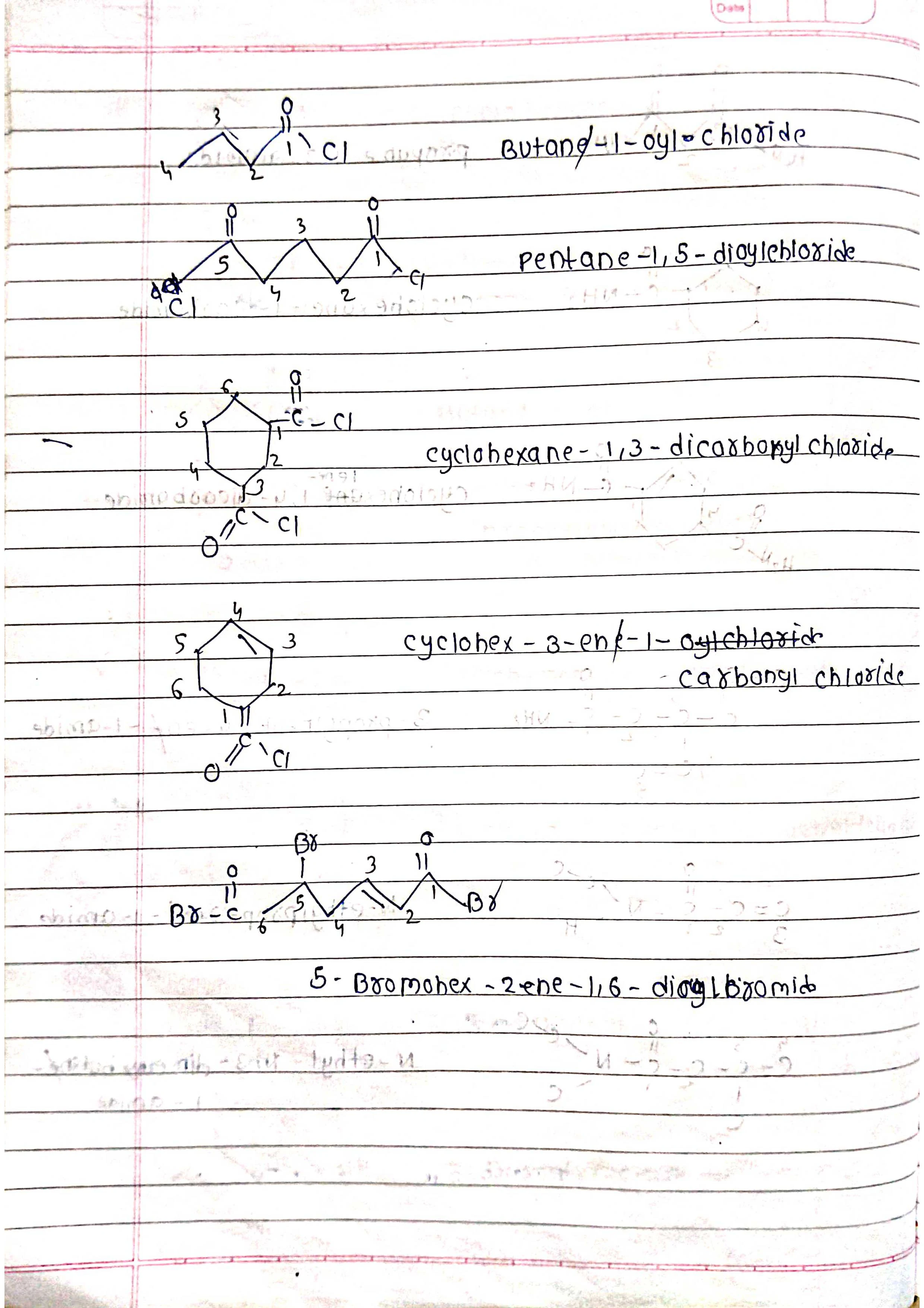
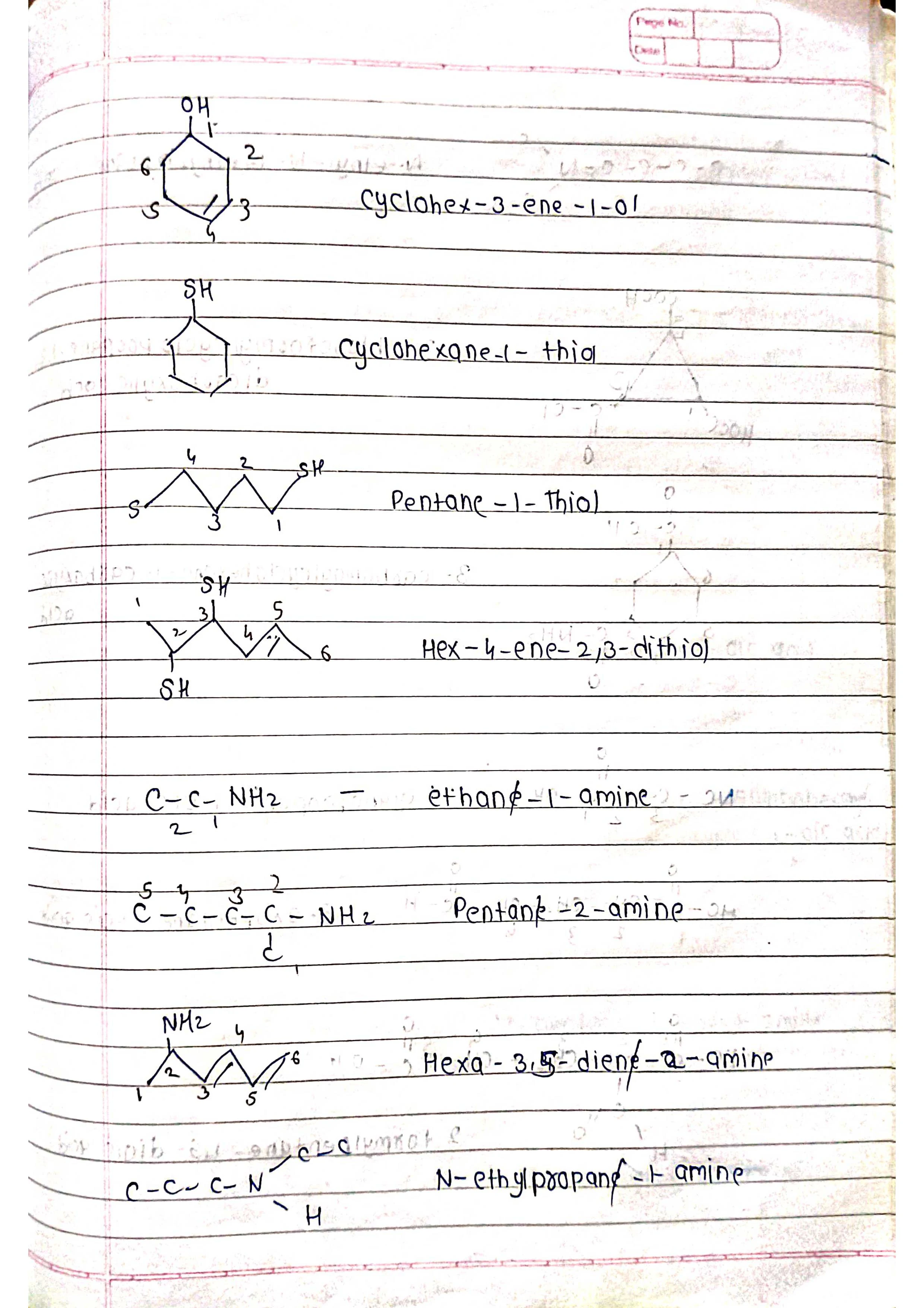
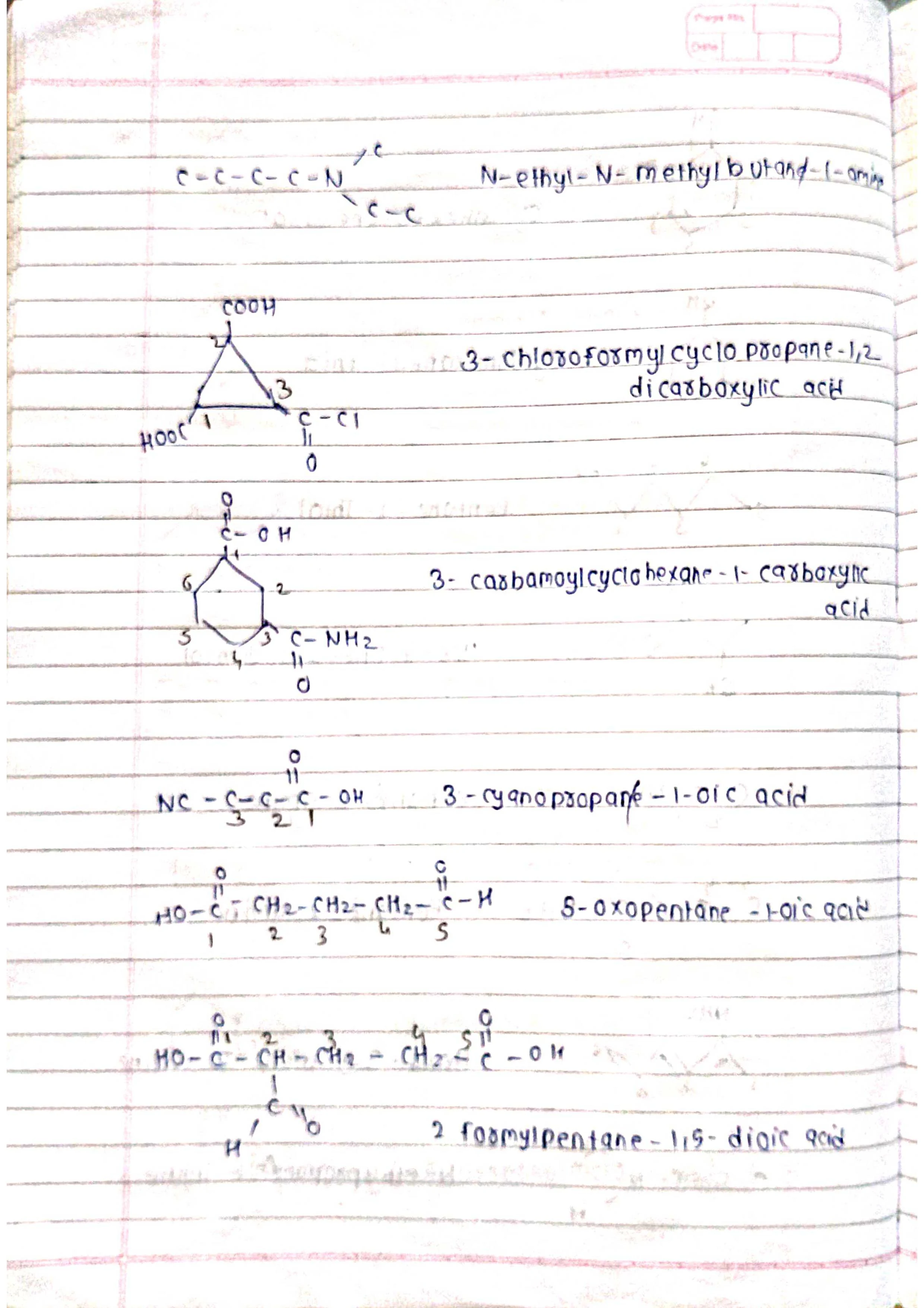
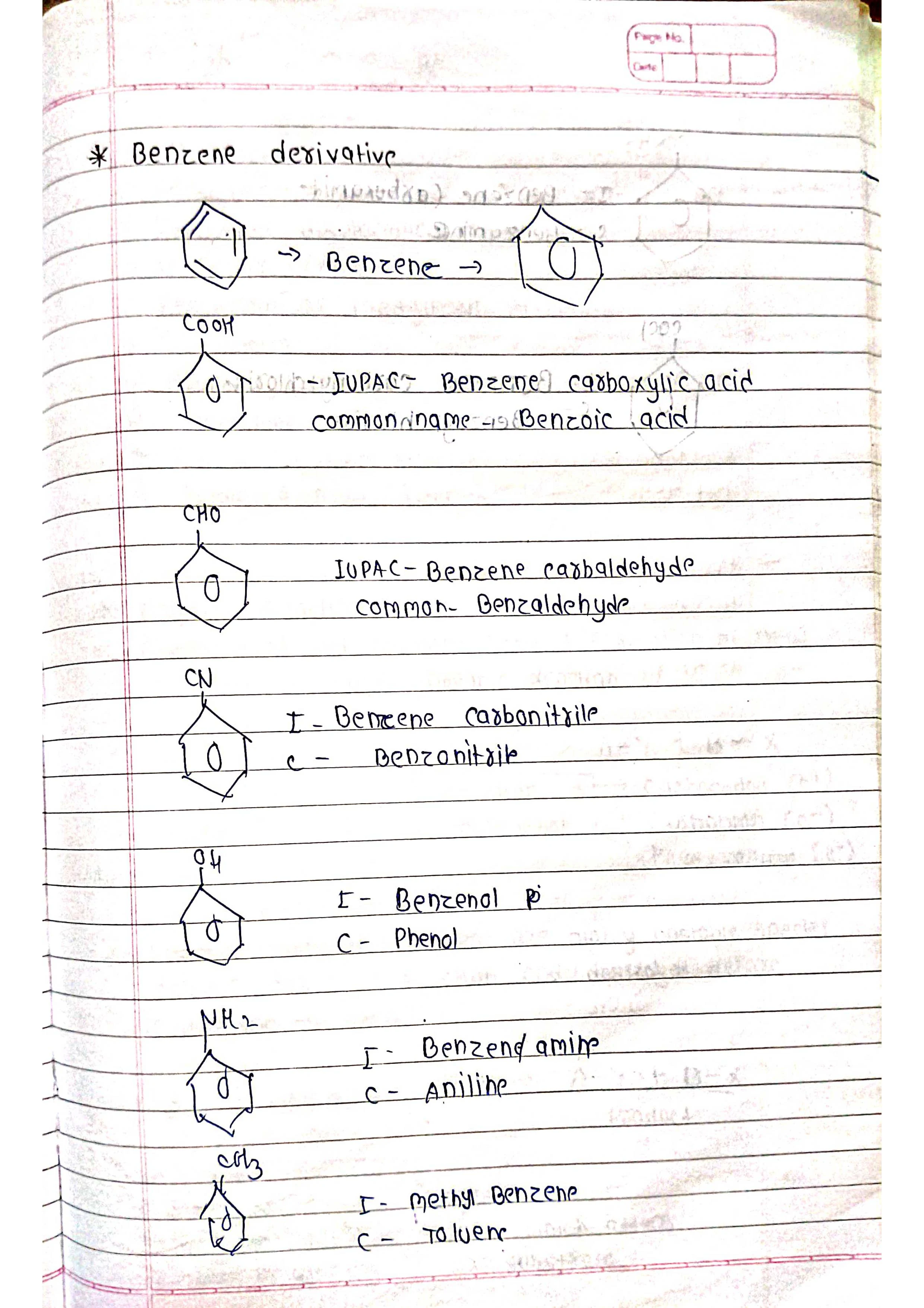
Based on parent chain: The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms forms the base name.
Functional groups: Different functional groups have specific suffixes attached to the base name.
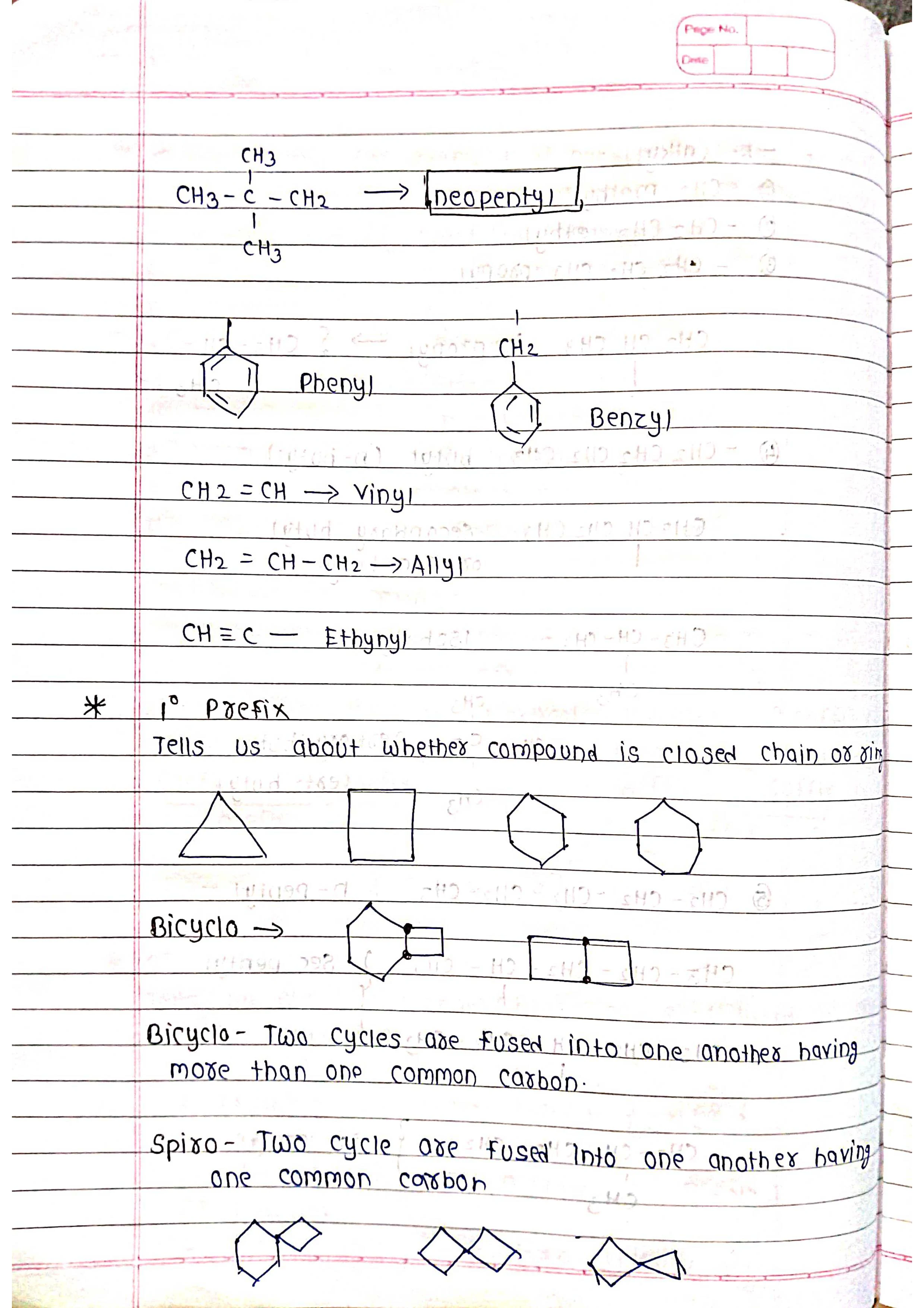
Substituents: Other atoms or groups attached to the chain are named as prefixes.
Priorities: Functional groups and substituents have priorities to determine their order in the name.
IUPAC Nomenclature - Steps for Naming
Identify the parent chain: Choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms.
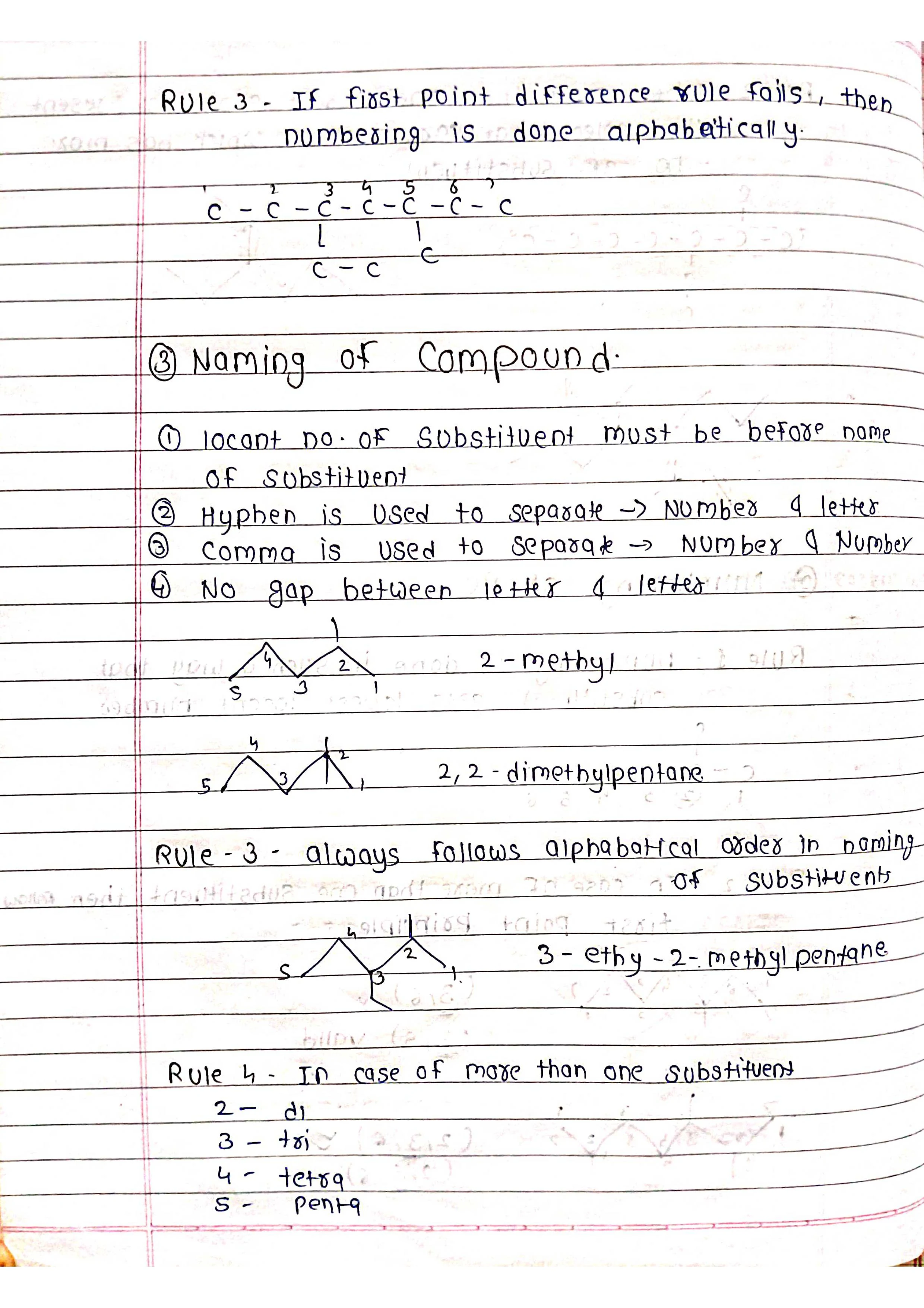
Number the chain: Start numbering from the end closest to a functional group (if present).
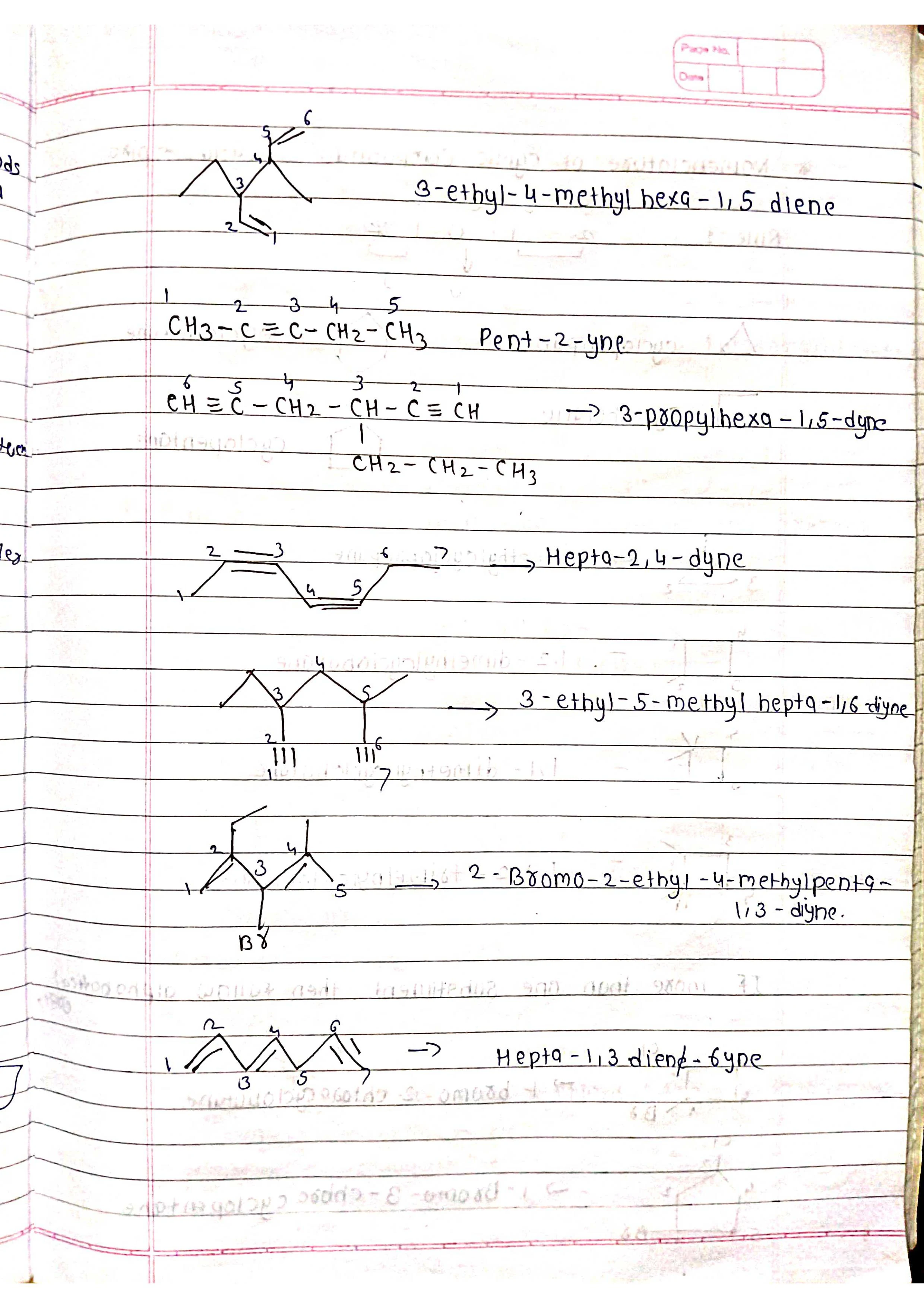
Identify functional groups: Assign suffixes based on priority (e.g., -ol for alcohol, -one for ketone).
Identify substituents: Name and number them based on their position on the chain (e.g., chloro-, 2-methyl-).
Assemble the name: Combine prefixes, numbers, and suffixes in the correct order.


![IUPAC Nomenclature - Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF]📚 IUPAC Nomenclature - Chemistry Short Handwritten Notes [PDF]📚](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgBAvFjzBhal9BhuftkSY9z_MMVoEltXsAtobooaWSKUQRGPBQgkPx61oefhuTvM9PiwQ507upnCve-Kzxeg1SIQYnwaYA5GF9GHnp7lHjT8hJIO8LzbS2wqtd7jfGY-2y2nYouR-8u8okSfopzAfI0XRLdTOnbWumnw7lVCiRtRzOYjnvvwSgLmX4aPUc/s16000-rw/IUPAC%20Nomenclature%20-%20Chemistry%20Short%20Handwritten%20Notes%20%5BPDF%5D%F0%9F%93%9A.jpeg)