Hydrocarbons are organic compounds made up solely of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms. They are the building blocks of many other organic molecules and play a crucial role in various fields, including fuels, plastics, and pharmaceuticals.
Hydrocarbon - Overview
➡️ Hydrocarbons are organic compounds made up only of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms.
➡️ They are the main constituents of petroleum and natural gas.
➡️ They serve as fuels, lubricants, and raw materials for various products like plastics, fibers, rubbers, solvents, and explosives.
Types of Hydrocarbons:
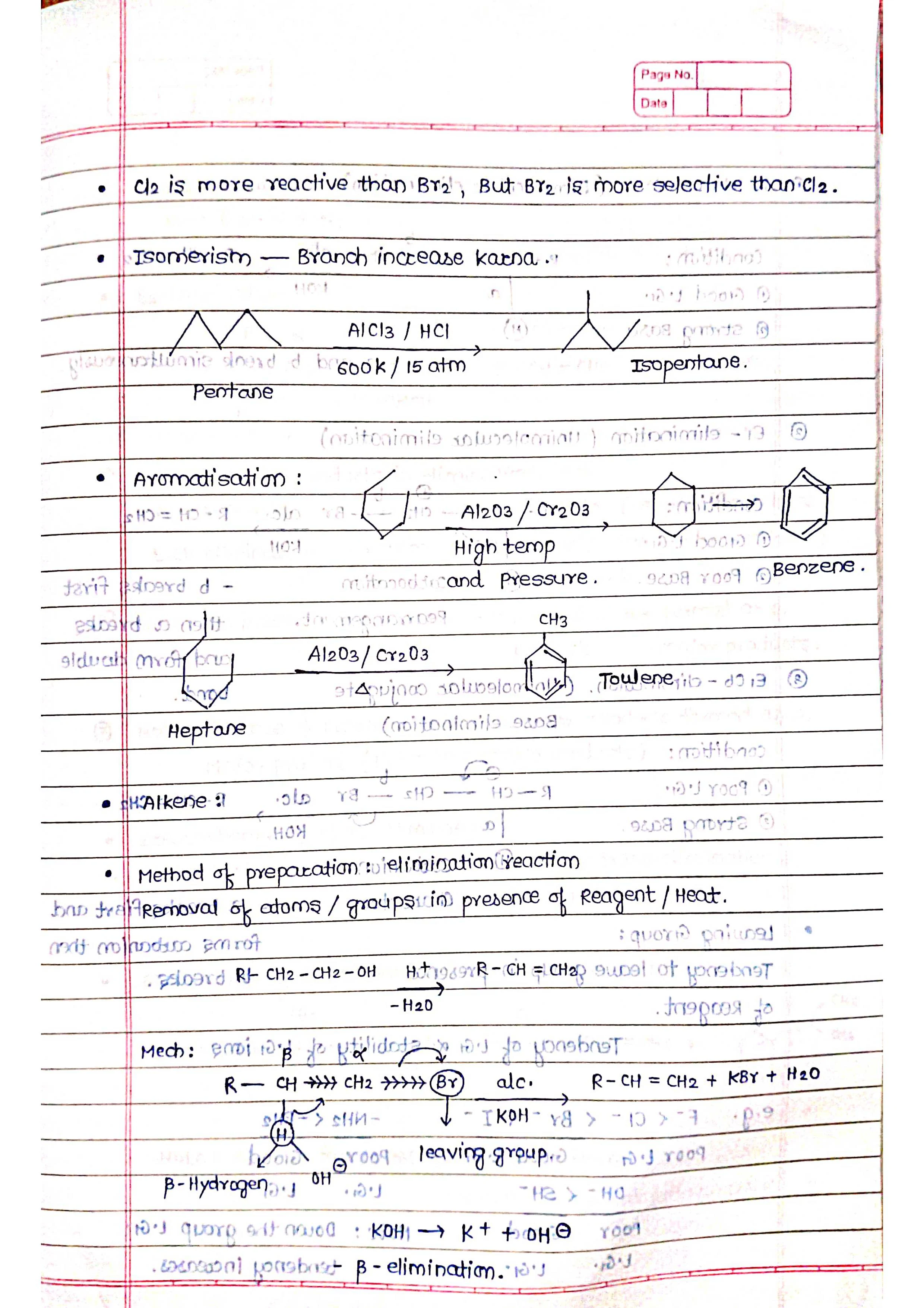
➭ Alkanes:
Saturated hydrocarbons (only single C-C bonds).
General formula: CnH2n+2 (n = number of carbon atoms).
Examples: methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8).
Properties: unreactive, low boiling points, good fuels.
➭ Alkenes:
Unsaturated hydrocarbons (at least one C=C double bond).
General formula: CnH2n (n = number of carbon atoms).
Examples: ethylene (C2H4), propylene (C3H6).
Properties: more reactive than alkanes, undergo addition reactions.
➭ Alkynes:
Unsaturated hydrocarbons (at least one C≡C triple bond).
General formula: CnH2n-2 (n = number of carbon atoms).
Examples: acetylene (C2H2), propyne (C3H4).
Properties: even more reactive than alkenes, readily undergo addition reactions.
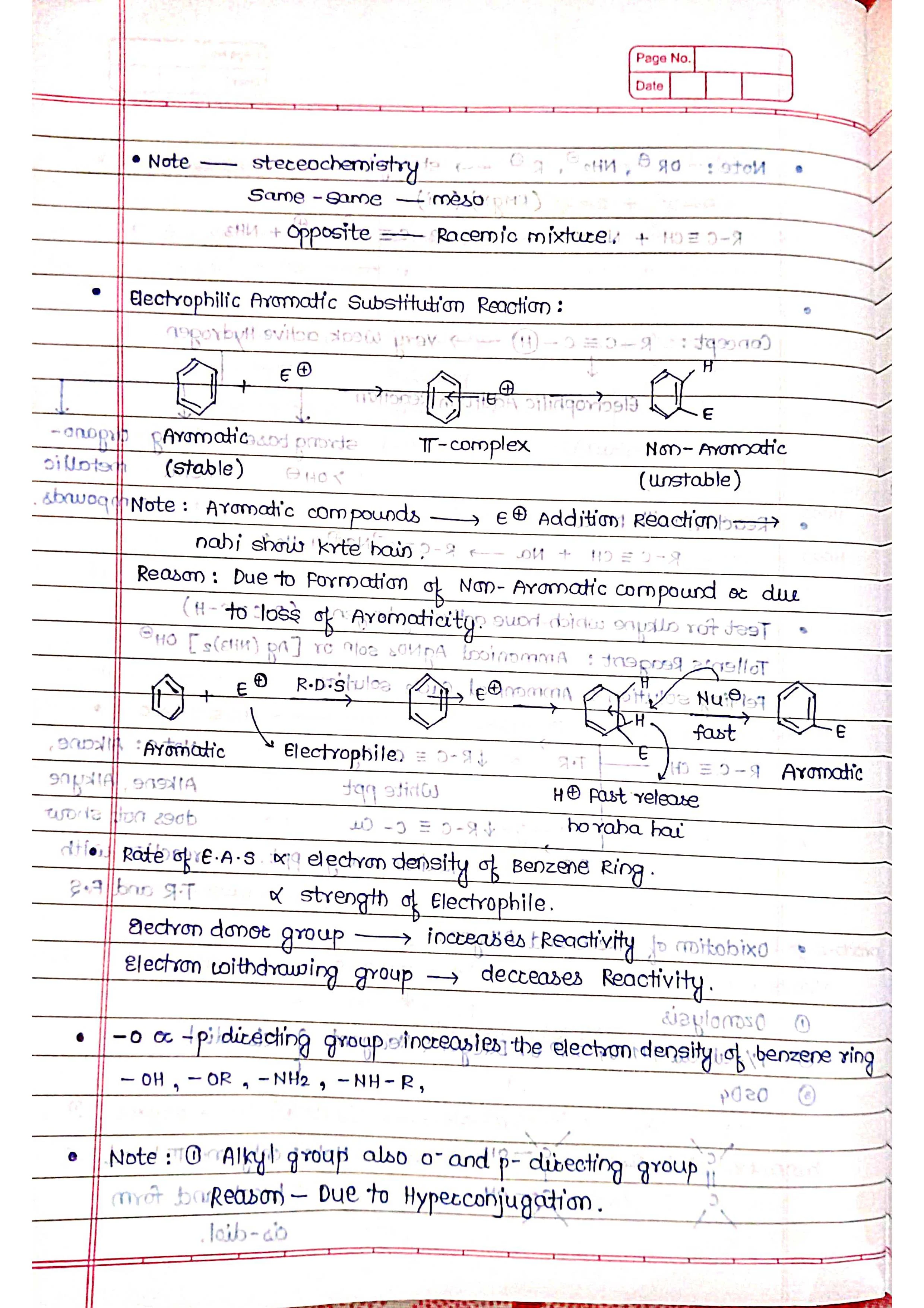
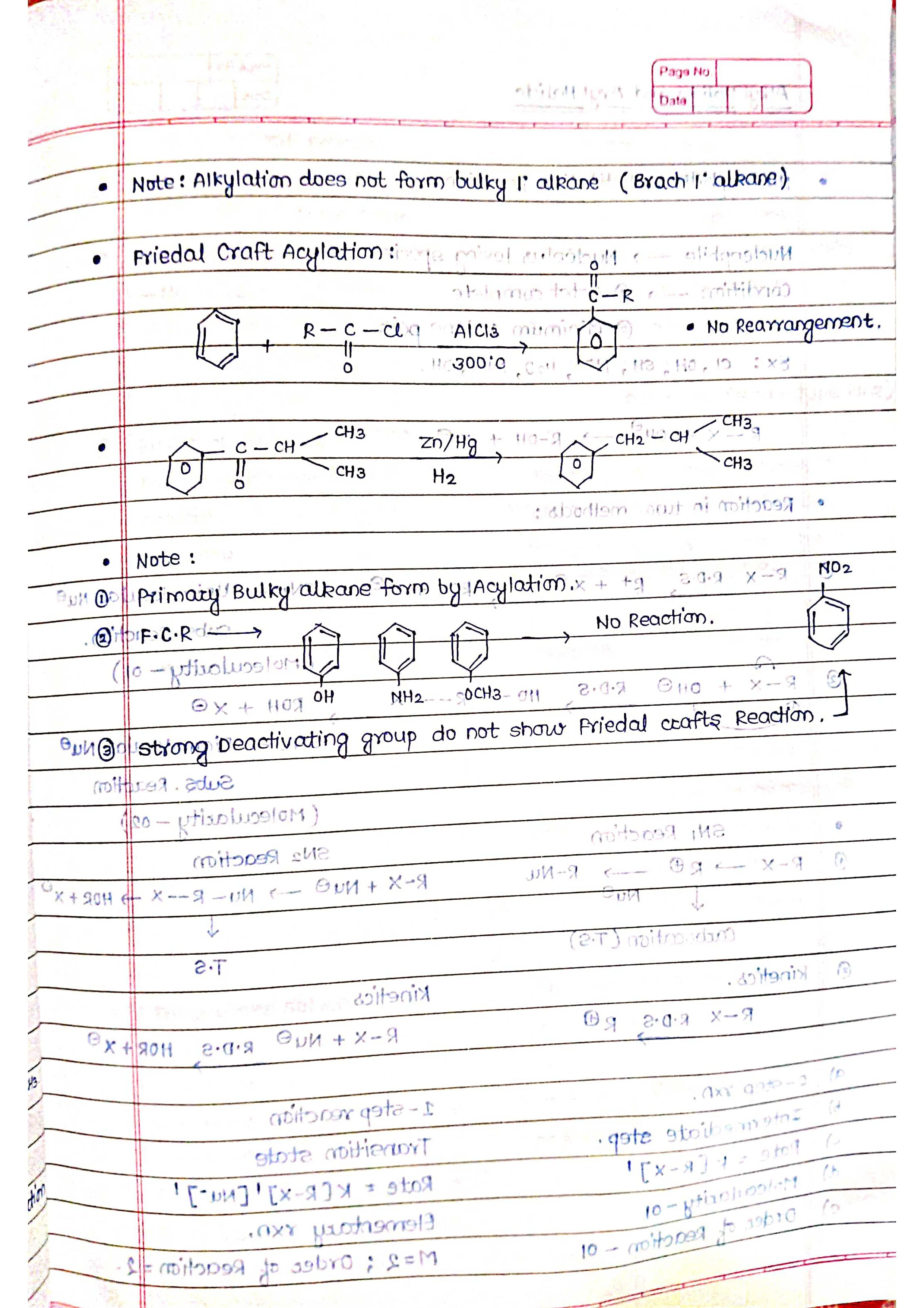
➭ Aromatic Hydrocarbons:
Characterized by a special ring structure called benzene ring.
Examples: benzene (C6H6), toluene (C7H8).
Properties: relatively stable due to their unique electron structure.
Chemistry Handwritten Short Notes 📚 for Class 11 & 12 | Free PDF Downloads