Redox Reactions - Redox is a shorthand term for reduction-oxidation reactions, which are a type of chemical reaction that involves the transfer of electrons between atoms.
In a redox reaction, one atom loses electrons (gets oxidized), while another atom gains electrons (gets reduced).
Key aspects of Redox Reactions:
➭ Electron transfer: In a redox reaction, electrons are transferred from one atom or molecule to another. The atom or molecule that loses electrons is oxidized, and the atom or molecule that gains electrons is reduced.
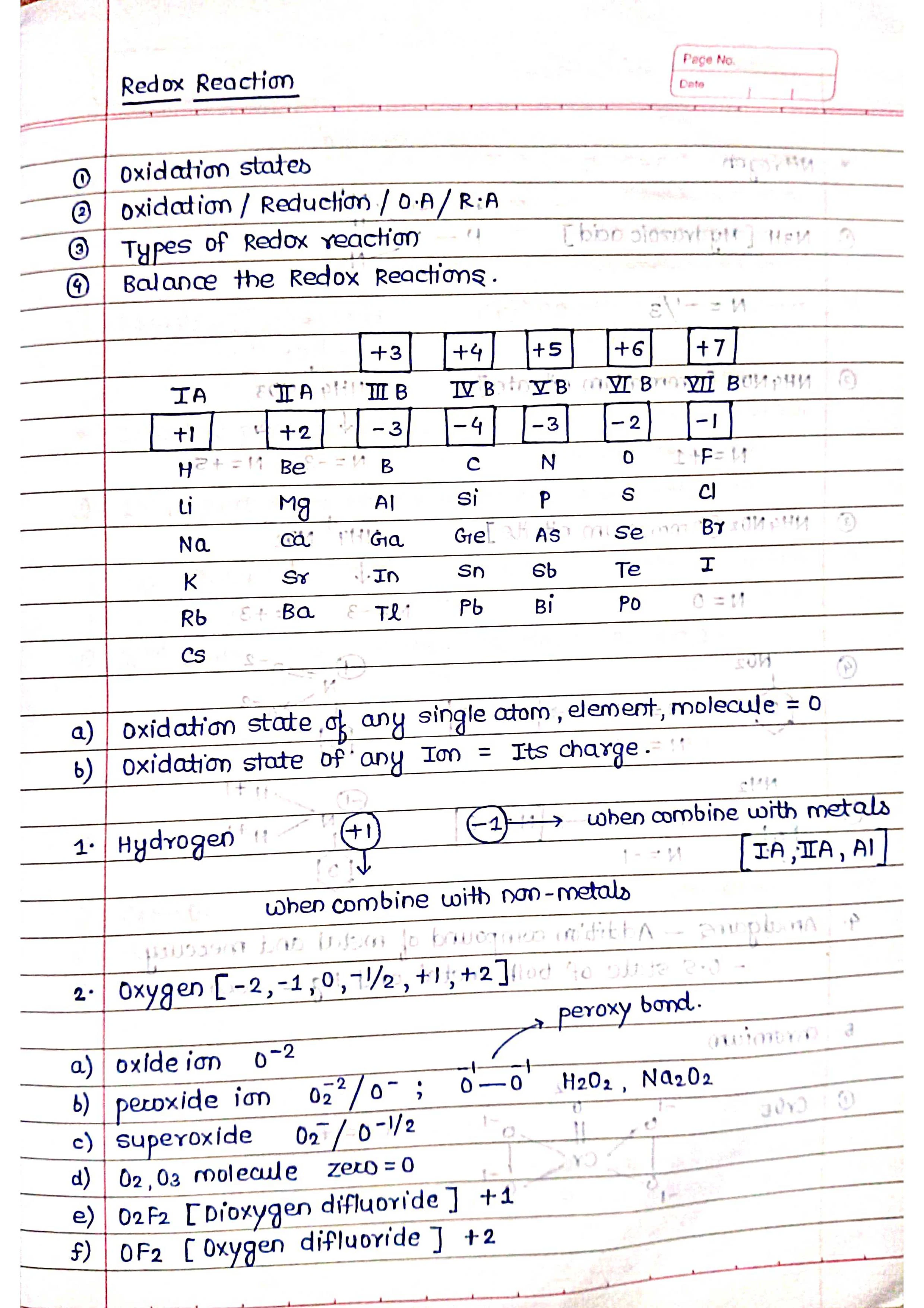
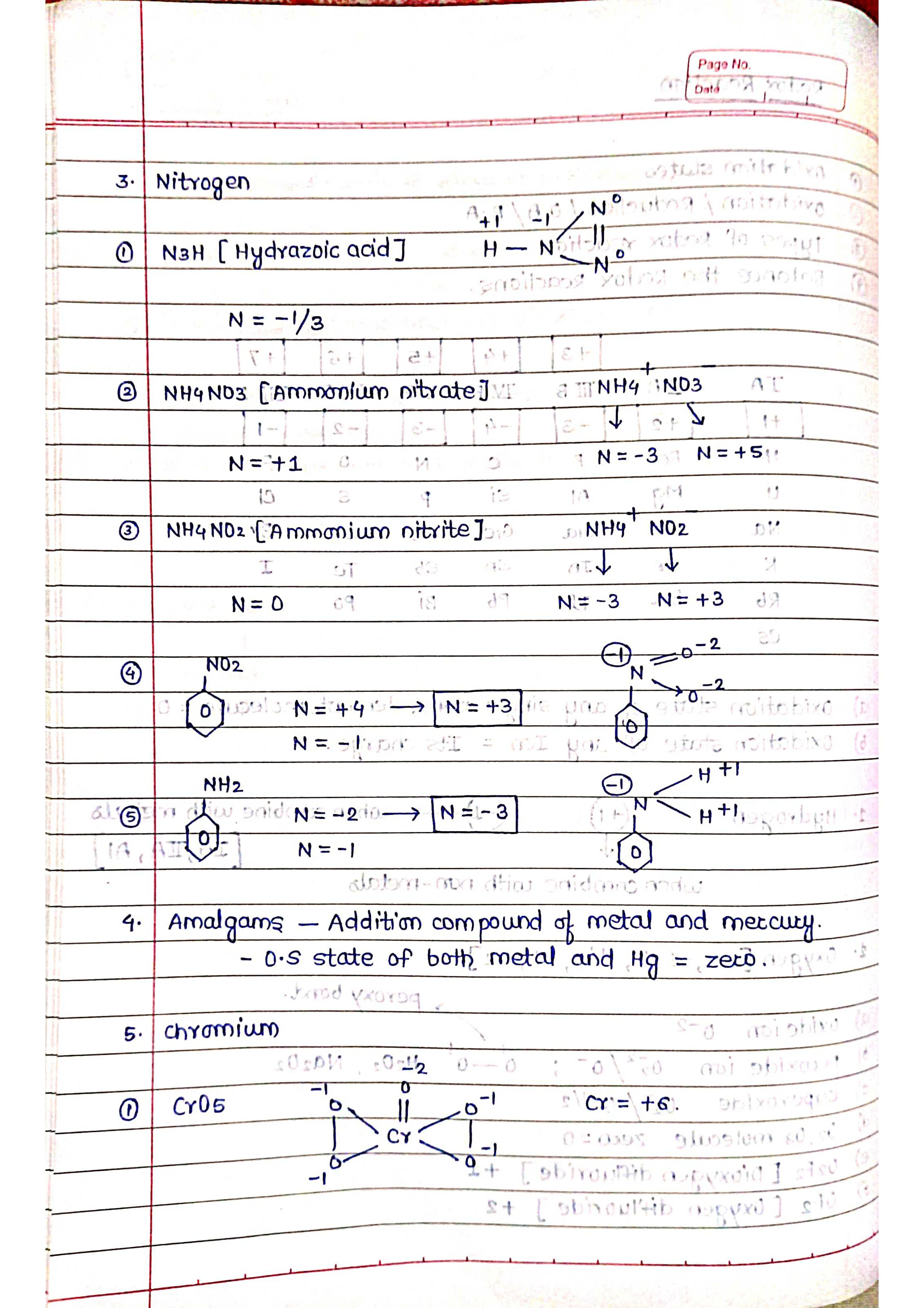
➭ Oxidation number: The oxidation number of an atom is the number of electrons that it has lost or gained in a compound, compared to its elemental state. Oxidation numbers can be positive, negative, or zero.
➭ Balancing redox equations: Redox equations must be balanced to ensure that the number of electrons lost is equal to the number of electrons gained.
Oxidation and Reduction
➭ Oxidation: When an atom loses electrons, its oxidation number increases. Oxidation can be thought of as the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state.
➭ Reduction: When an atom gains electrons, its oxidation number decreases. Reduction can be thought of as the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state.
Redox Reactions and Cells
Redox reactions are essential for the functioning of many biological processes, such as photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
They are also used in many technological applications, such as batteries and fuel cells.
Types of Redox Reactions:
➭ Single displacement reactions: In a single displacement reaction, one element replaces another element in a compound. For example, in the reaction between iron and copper sulfate, iron displaces copper from copper sulfate to form iron sulfate and copper metal.
➭ Double displacement reactions: In a double displacement reaction, the ions of two compounds interchange partners to form two new compounds. For example, in the reaction between sodium chloride and silver nitrate, sodium ions combine with nitrate ions to form sodium nitrate, and silver ions combine with chloride ions to form silver chloride.
➭ Combination reactions: In a combination reaction, two or more elements or compounds combine to form a single new compound. For example, in the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water.
➭ Decomposition reactions: In a decomposition reaction, a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler compounds or elements. For example, in the decomposition of calcium carbonate, calcium carbonate breaks down into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
Importance of Redox Reactions:
Redox reactions are important in many biological processes, such as cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
Redox reactions are also used in batteries, fuel cells, and other electrochemical devices.
Balancing Redox Reactions
Balancing redox reactions is important because it ensures that the number of electrons lost in the oxidation half-reaction is equal to the number of electrons gained in the reduction half-reaction.
Chemistry Short Notes 📚⌛
1. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Short Notes 📚
2. Atomic Structure — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
3. Periodic table — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
4. Chemical Bonding — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
5. States of matter — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
6. Thermodynamics — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
7. Chemical Equilibrium — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
8. Ionic Equilibrium — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
9. P-Block Elements 1 - Chemistry Short Notes 📚
10. Hydrogen — Chemistry Short Notes 📚
11. S-Block Elements - Chemistry Short Notes 📚